Chemistry and Chemists № 1 2025
Journal of Chemists-Enthusiasts
| Content | Chemistry experiments - video | Physics experiments - video | Home Page - Chemistry and Chemists |
|
Chemistry and Chemists № 1 2025 Journal of Chemists-Enthusiasts |
Dissolution of Nickel in Aqueous Ammonia Solution Volodymyr M. Viter |
|
Having noticed a mistake in the text, allocate it and press Ctrl-Enter
As is known, metallic copper reacts with an aqueous solution of ammonia in the presence of air. The metal is oxidized and dissolves, forming the complex ion [Cu(NH3)4]2+ [1]. This reaction turns the colorless solution an intense blue. Copper alloys, such as brass, exhibit similar behavior.
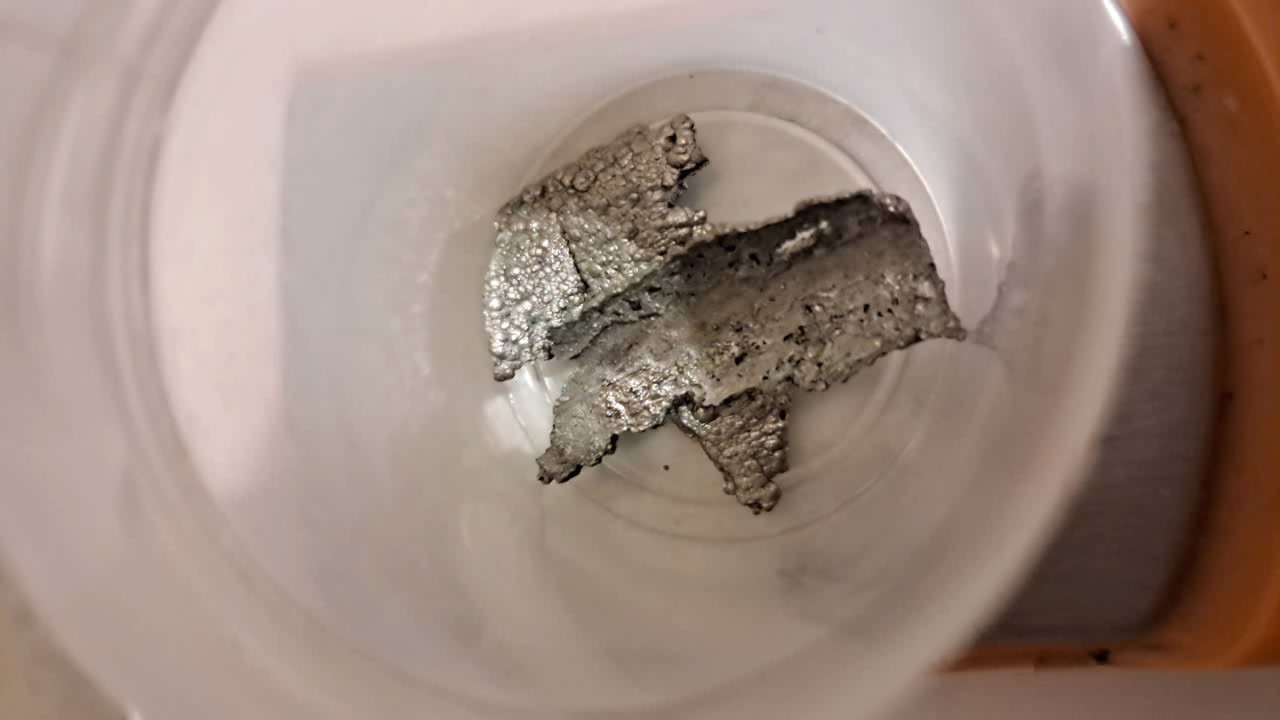
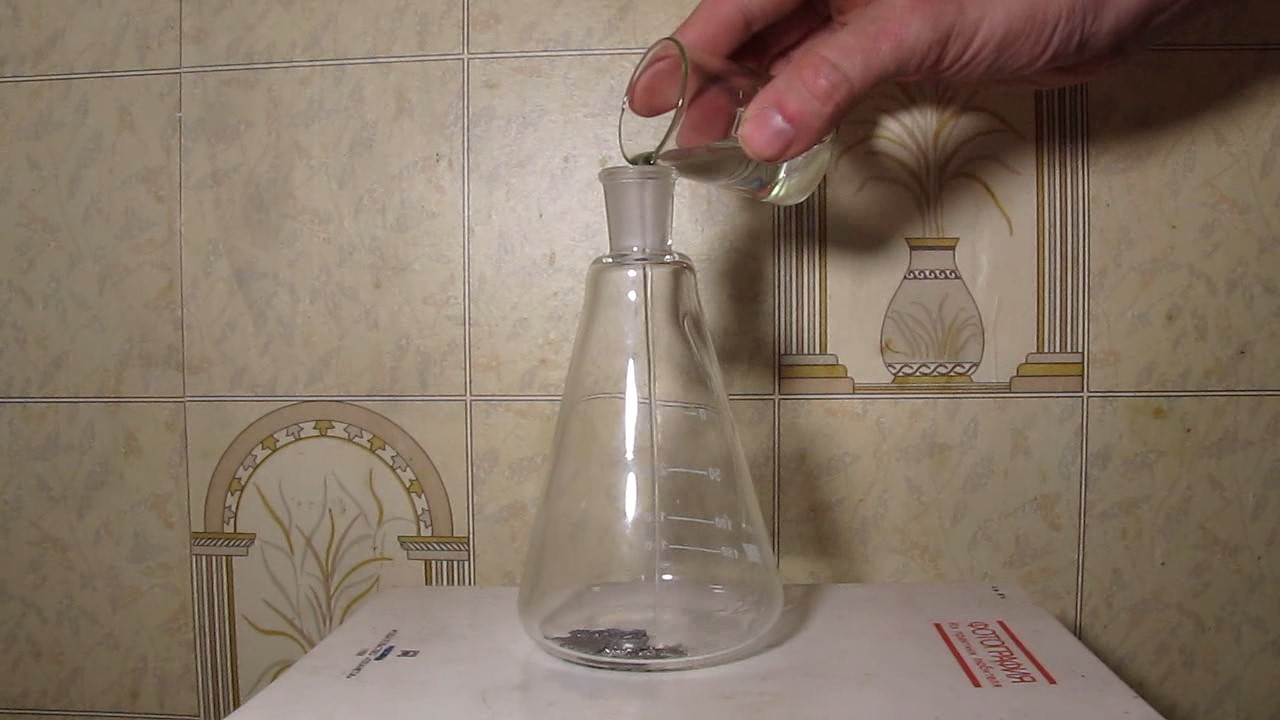
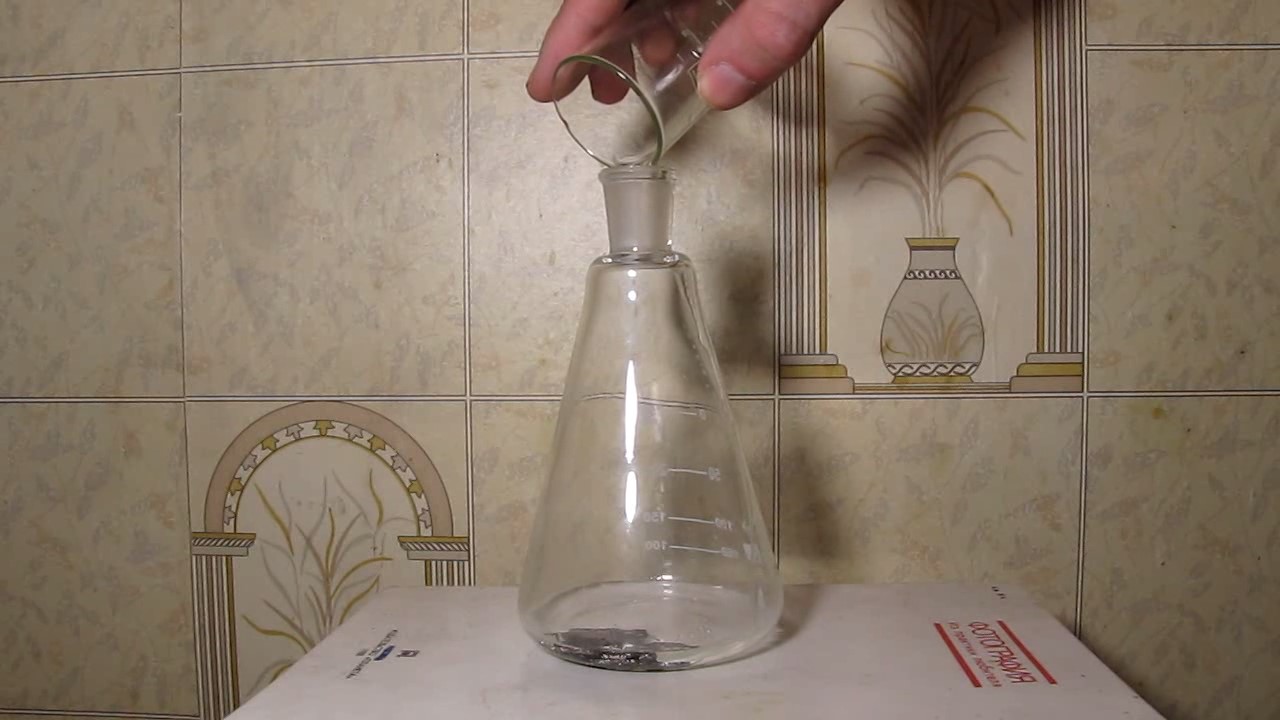
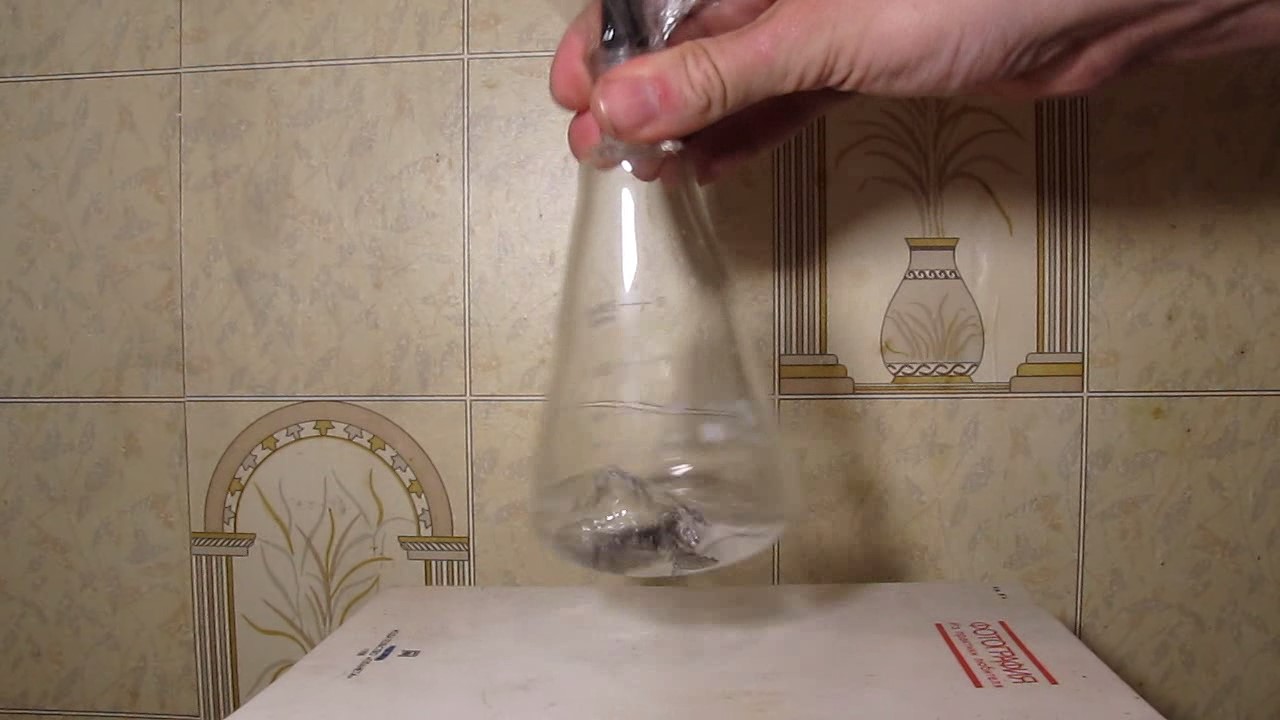
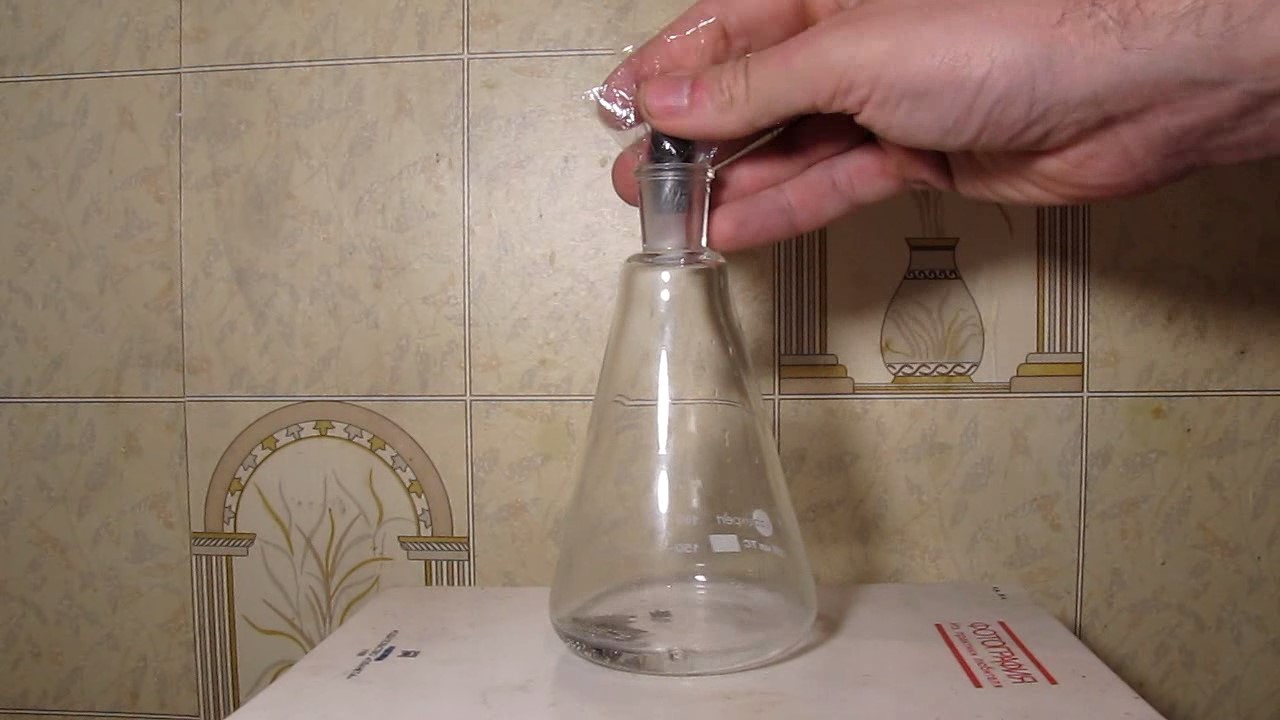
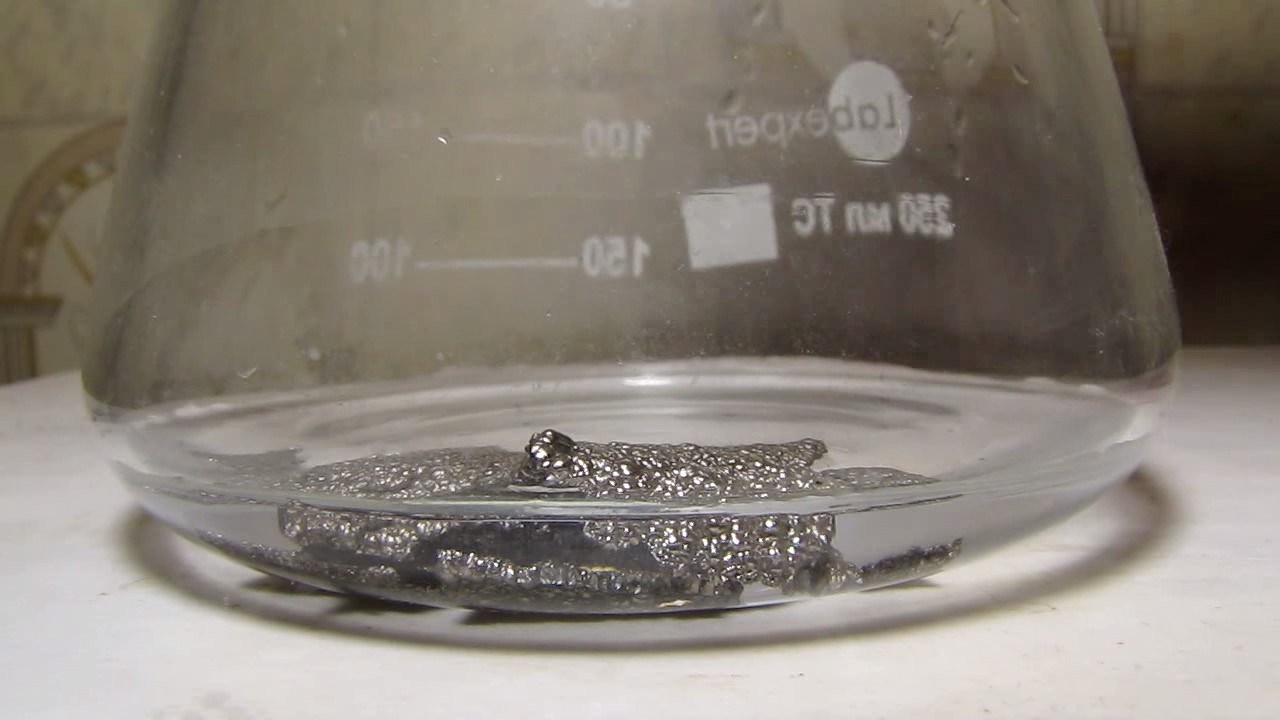
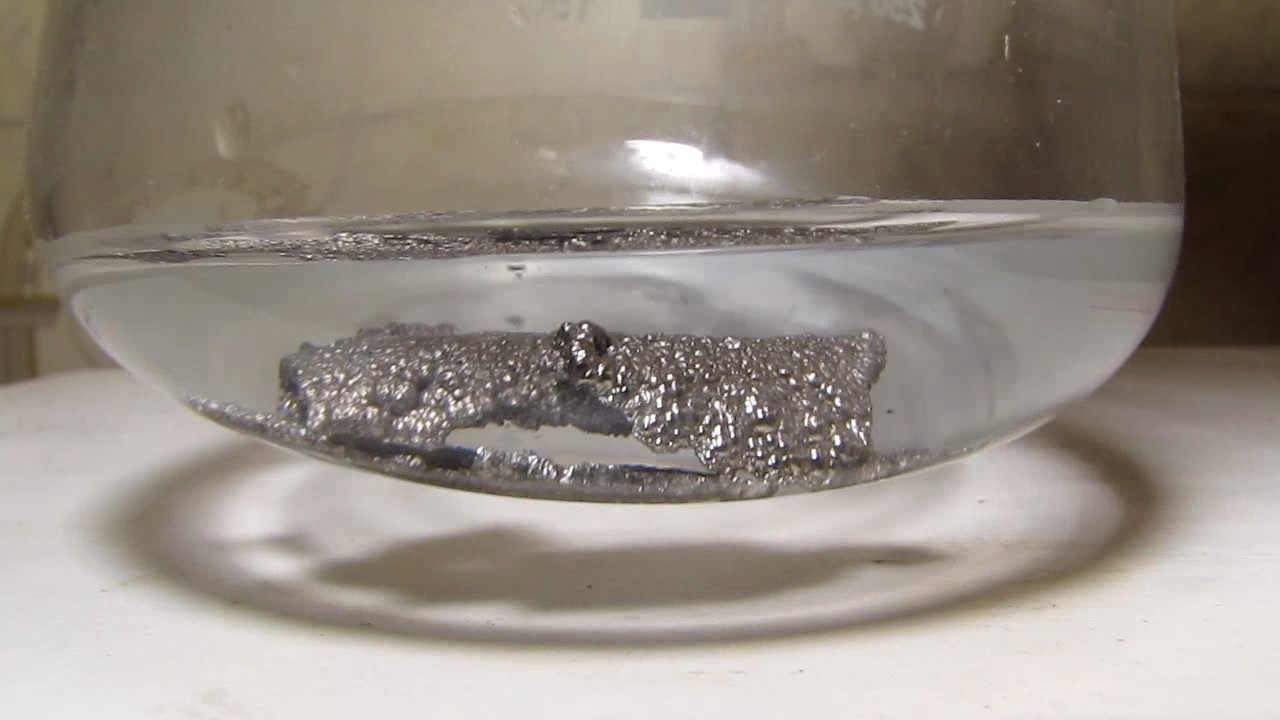
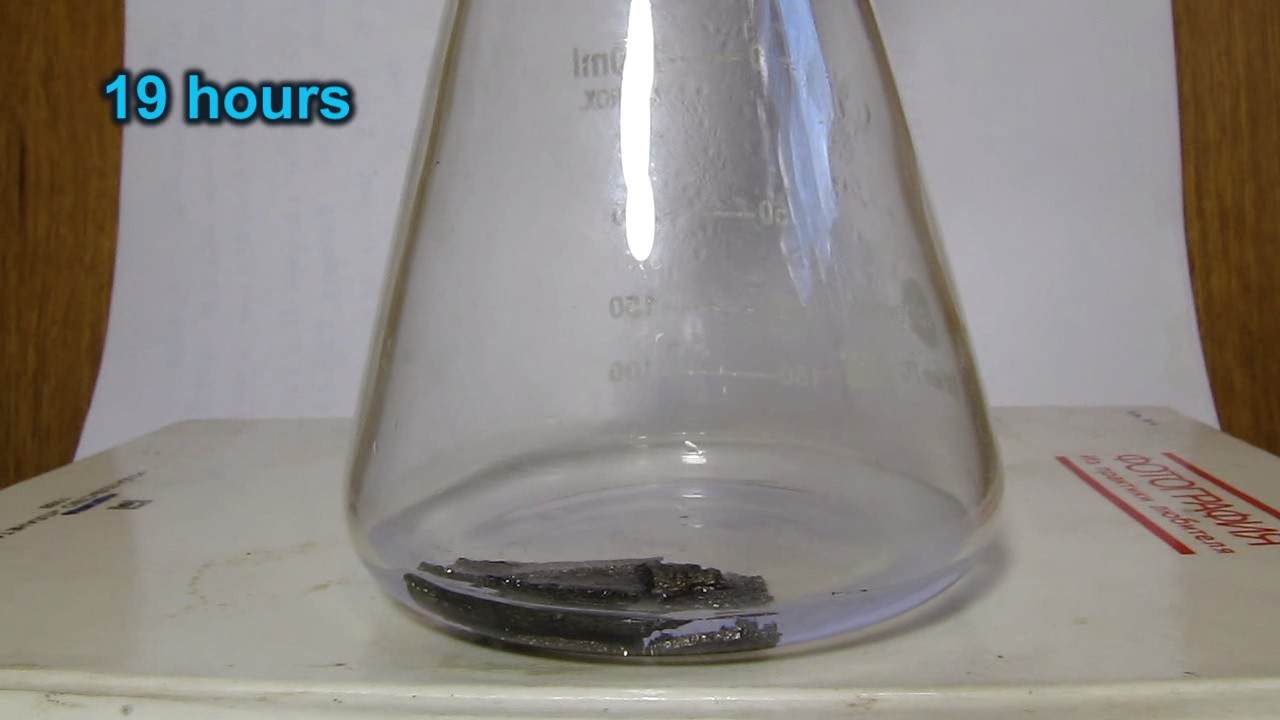
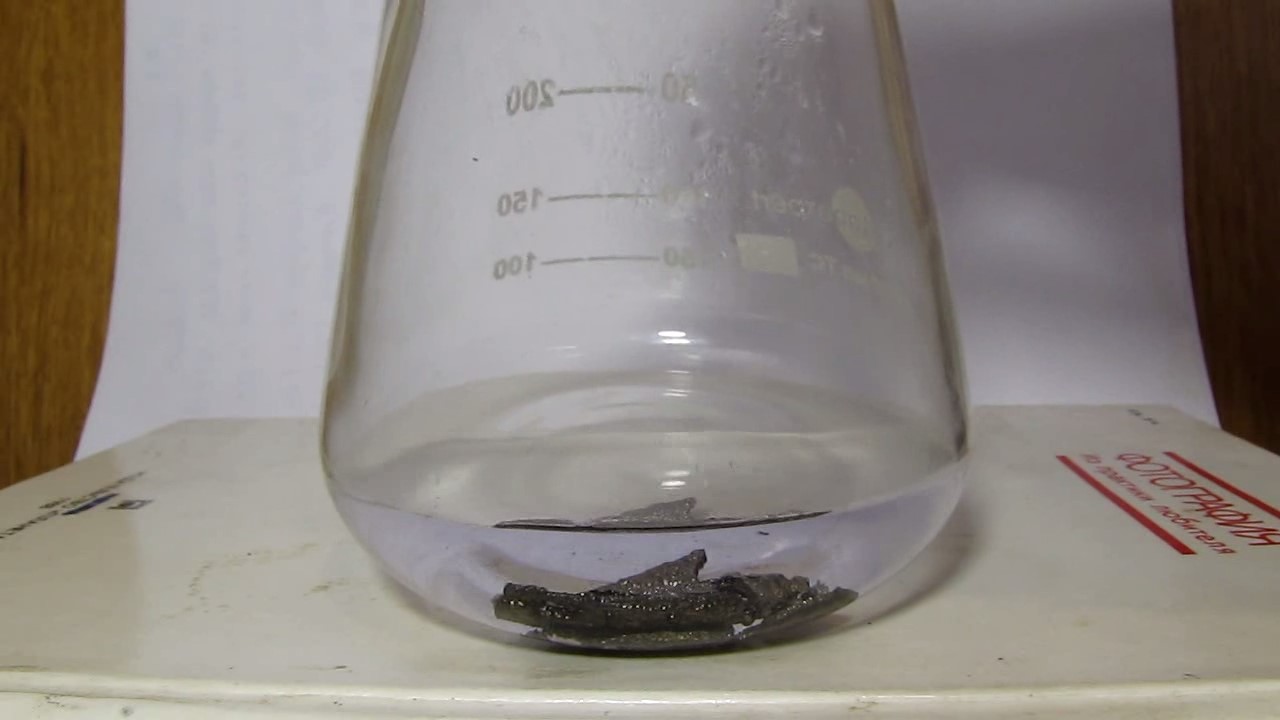
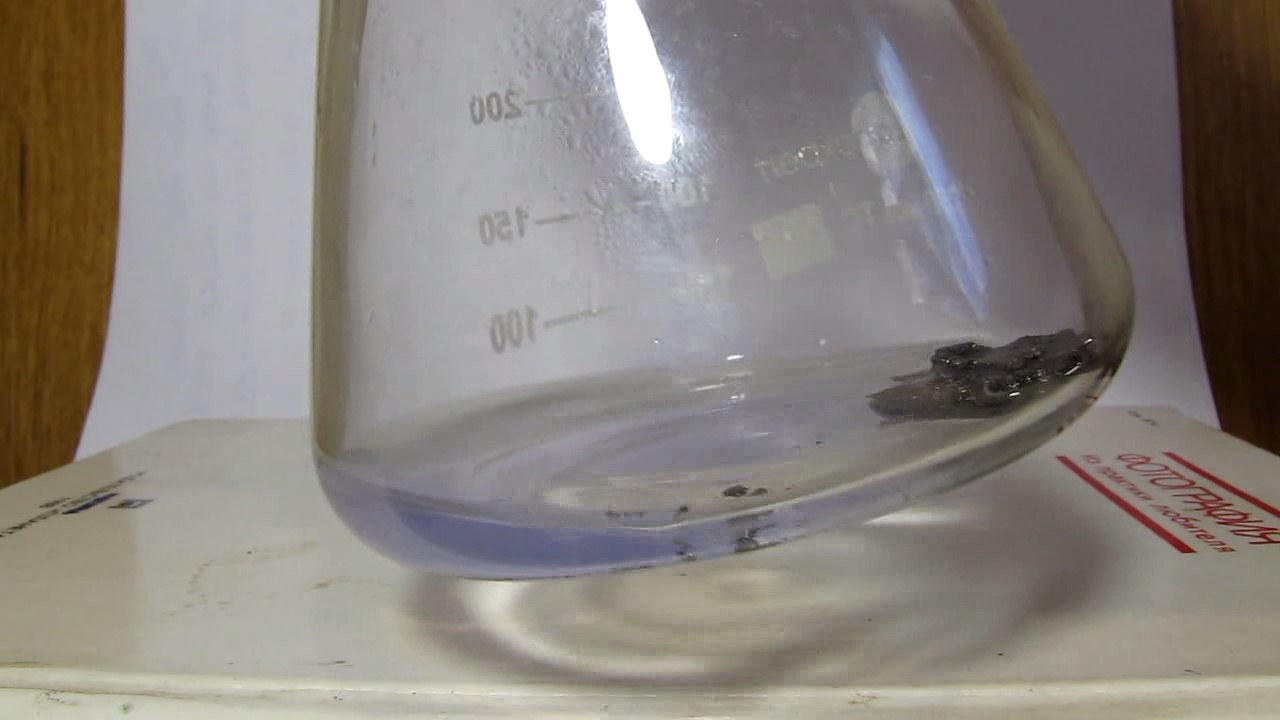
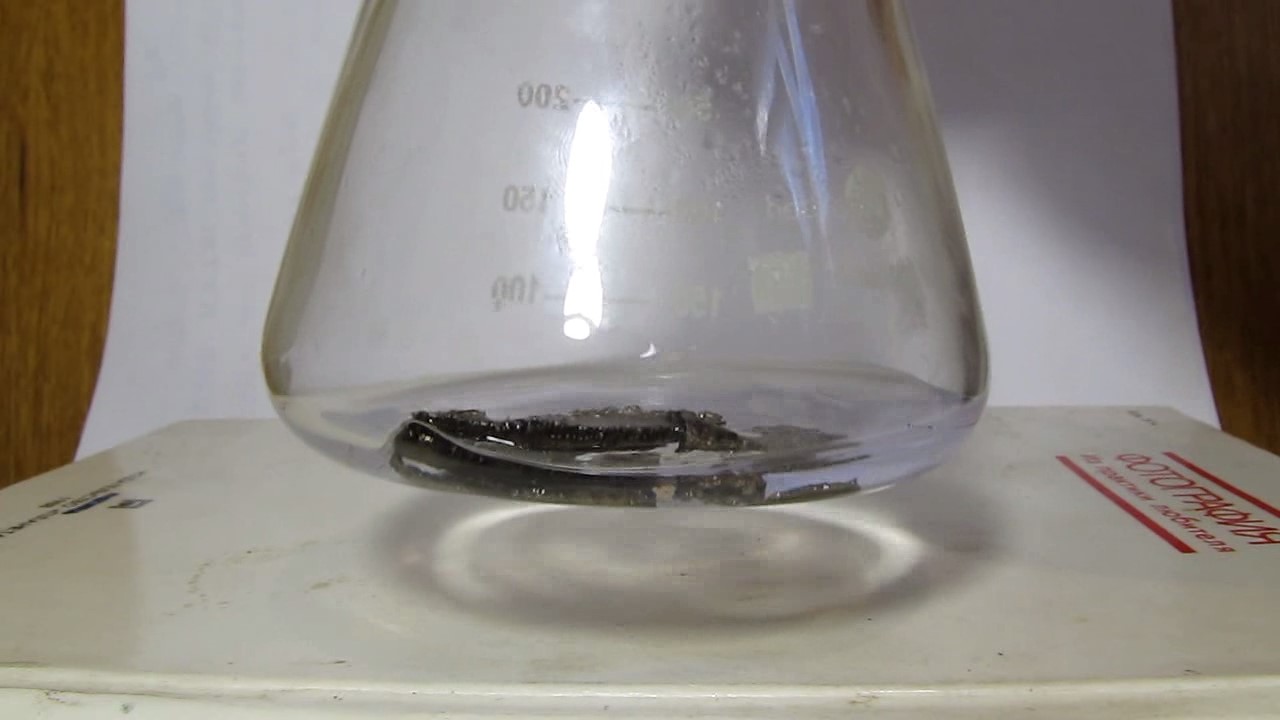
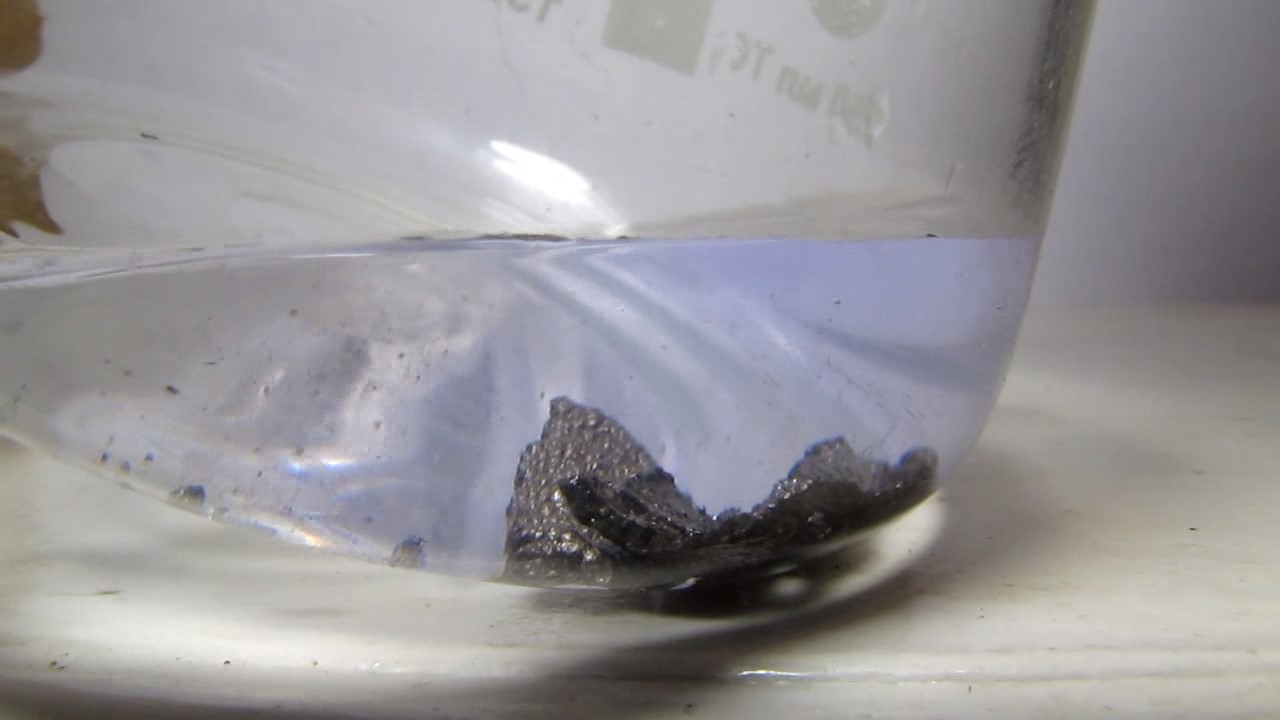
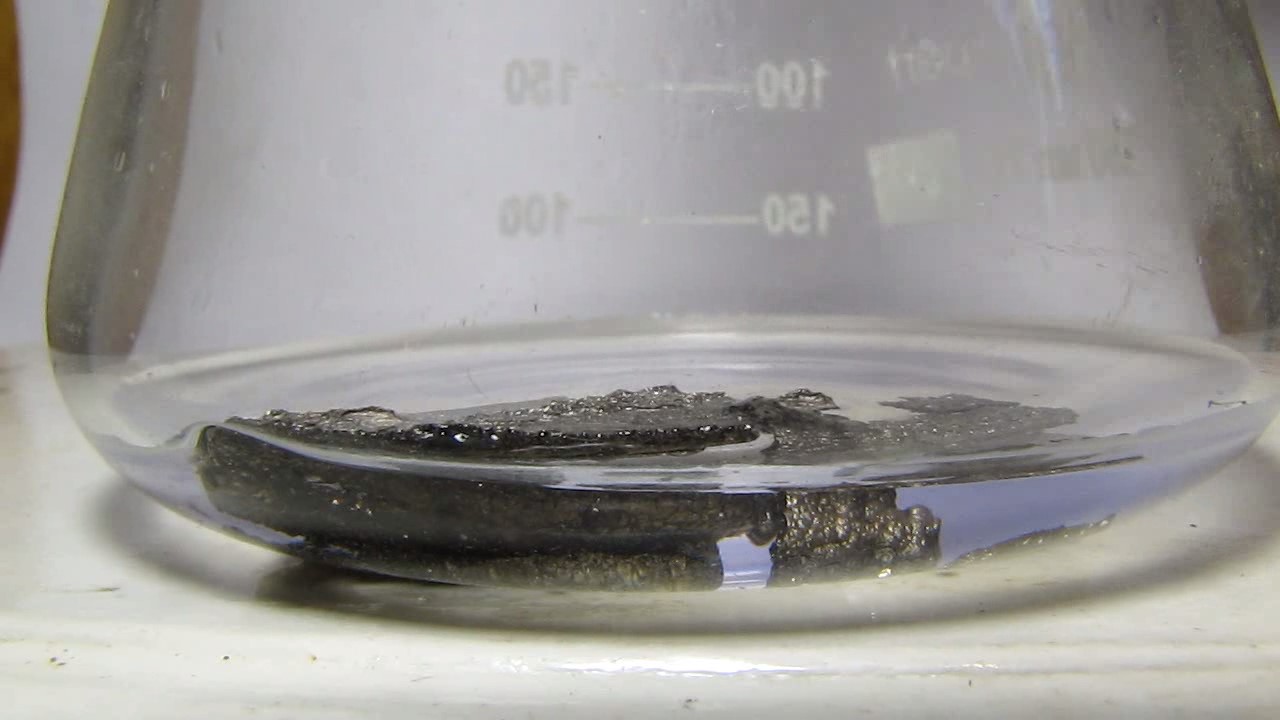
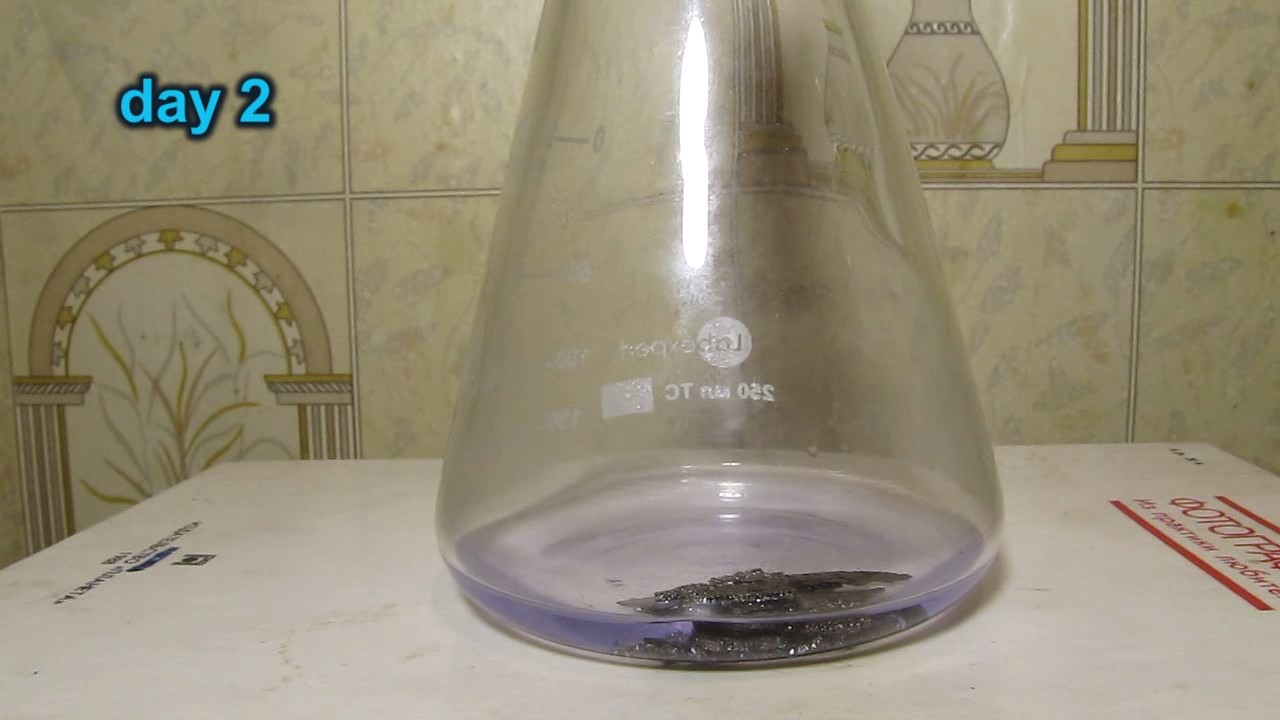
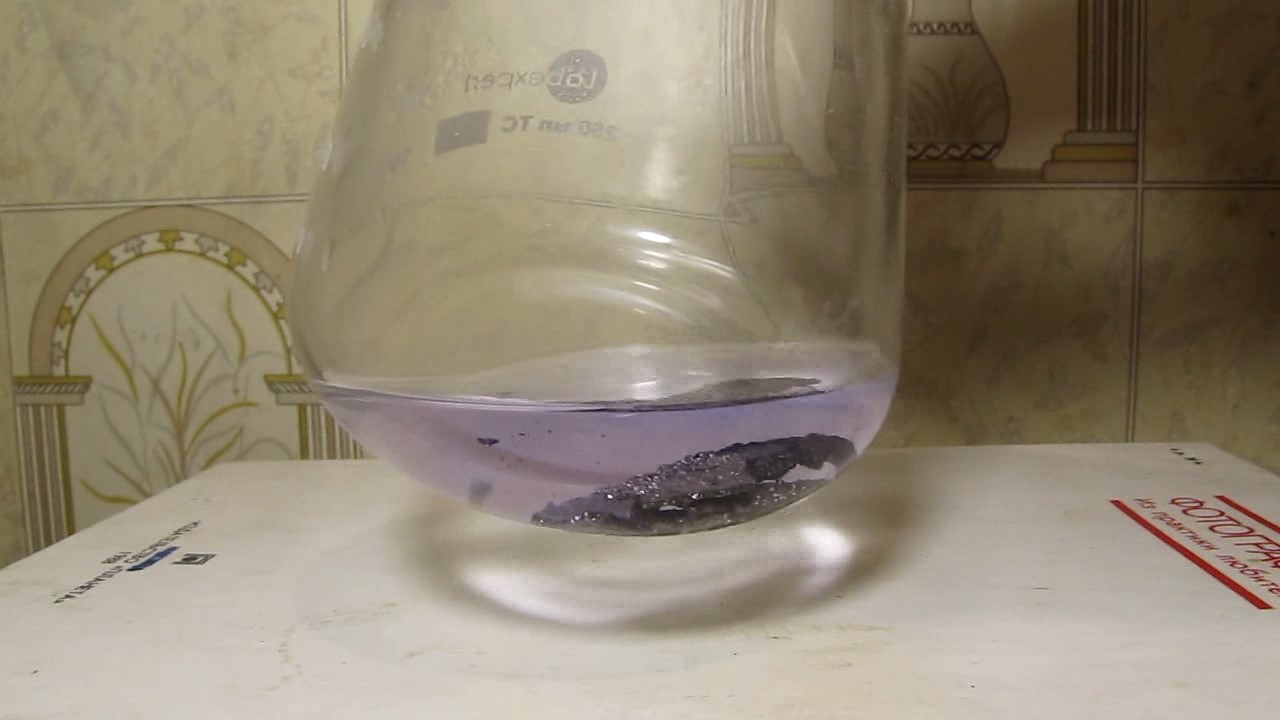
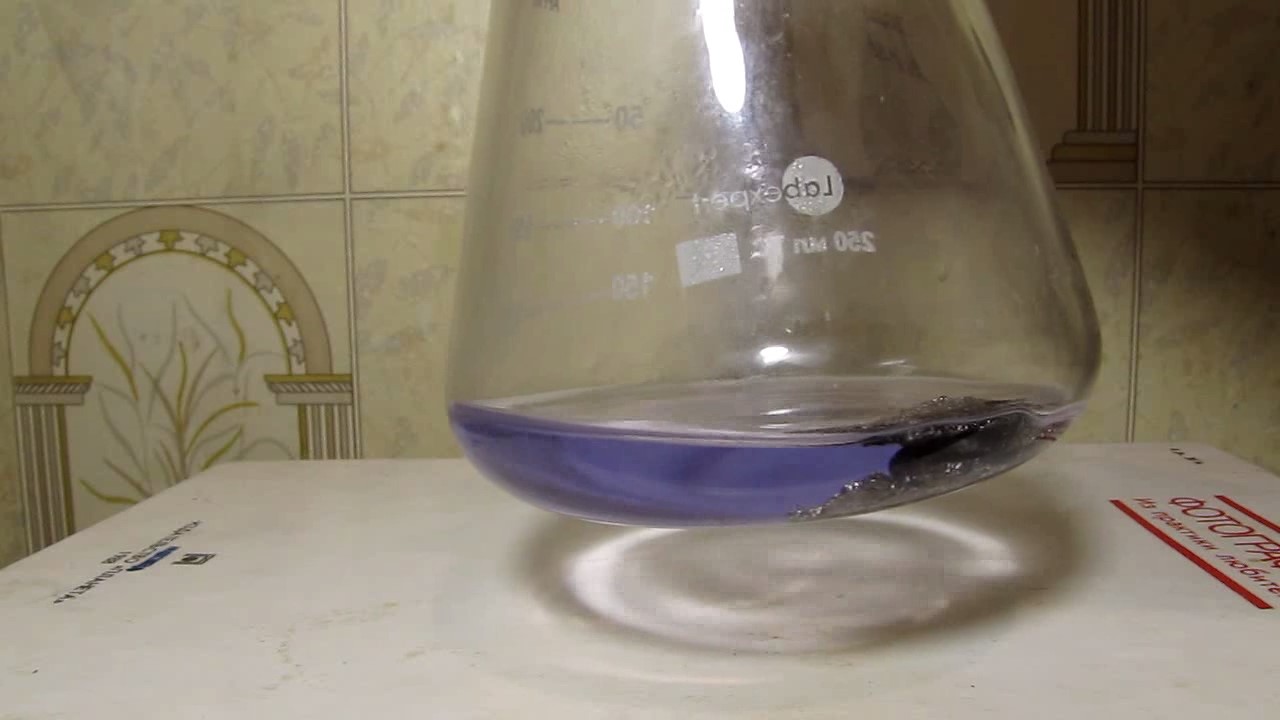
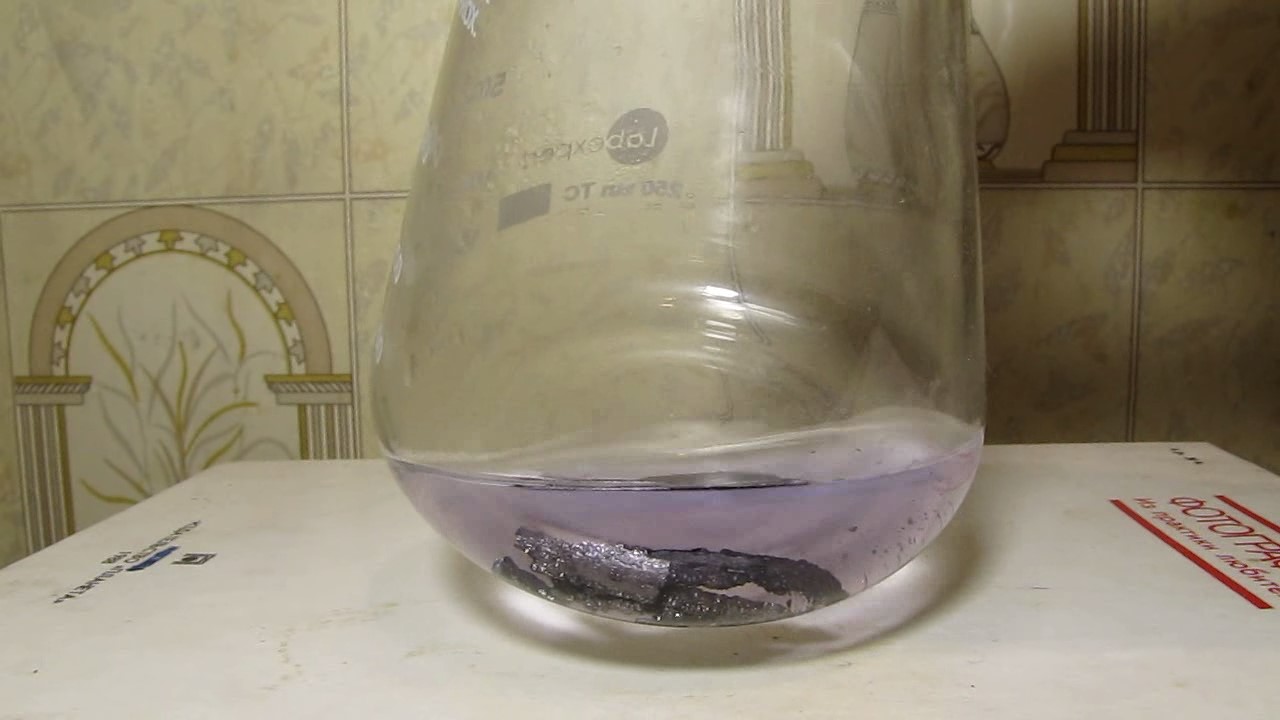
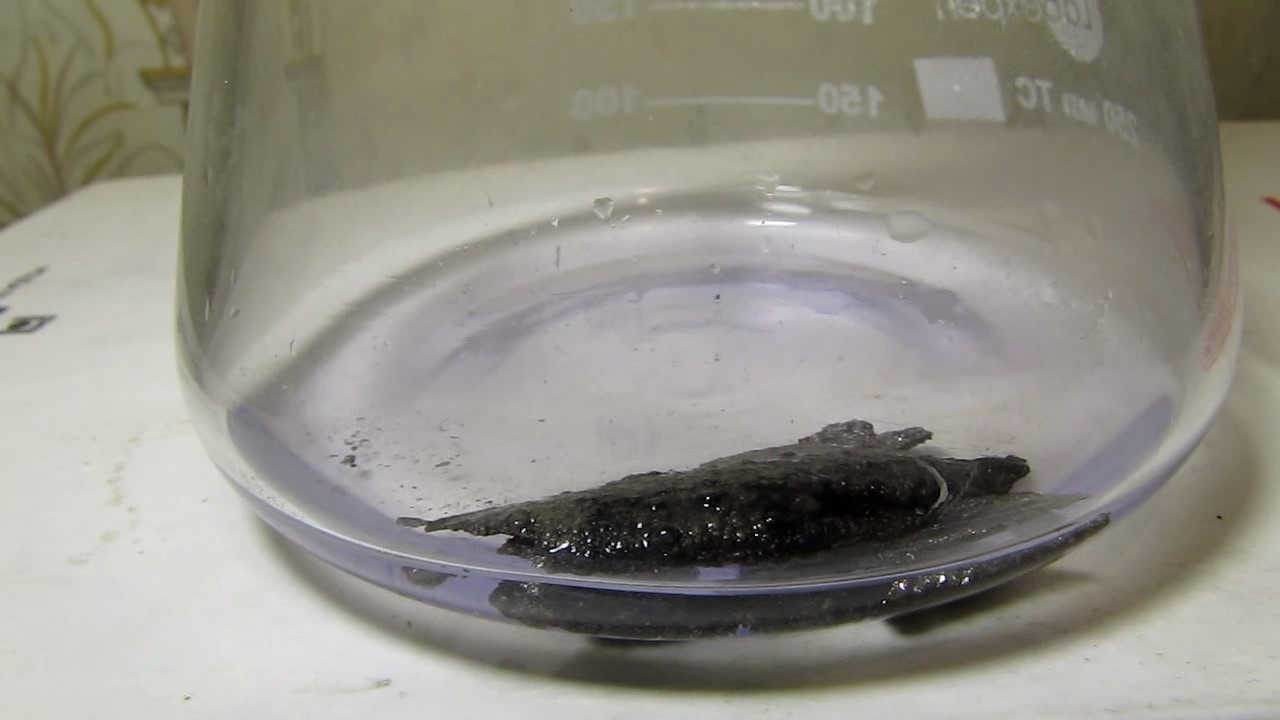
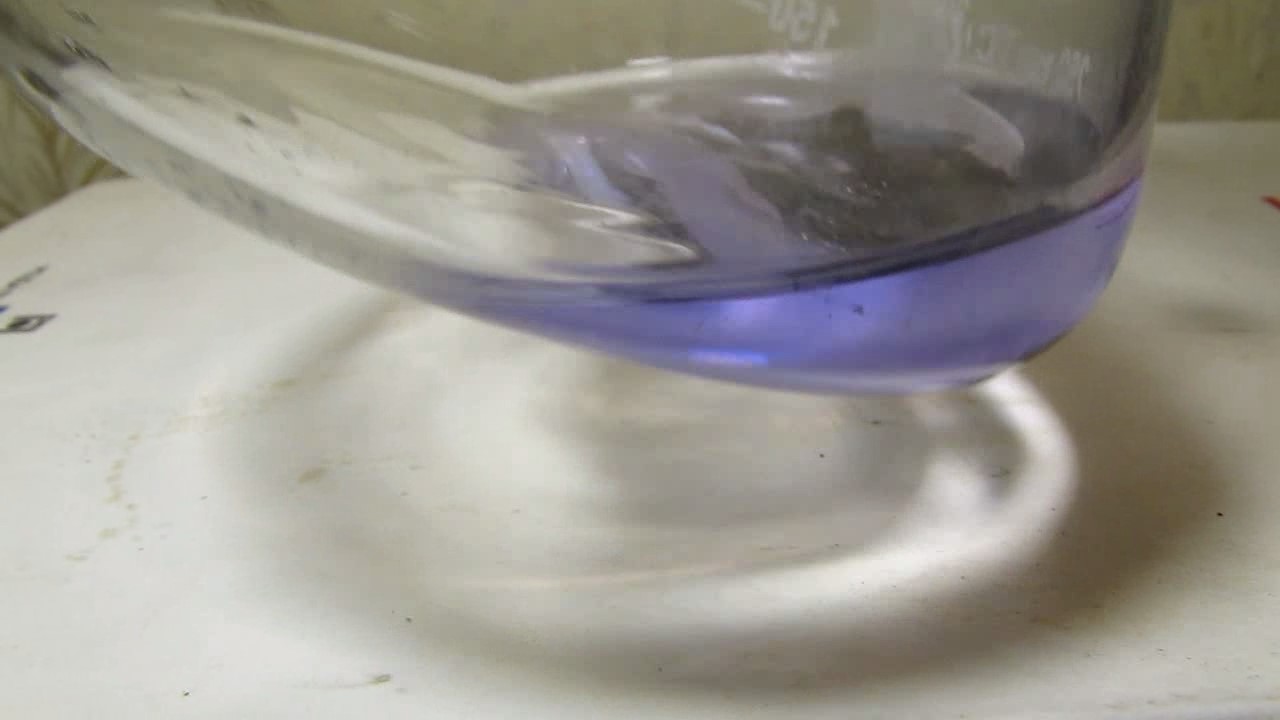
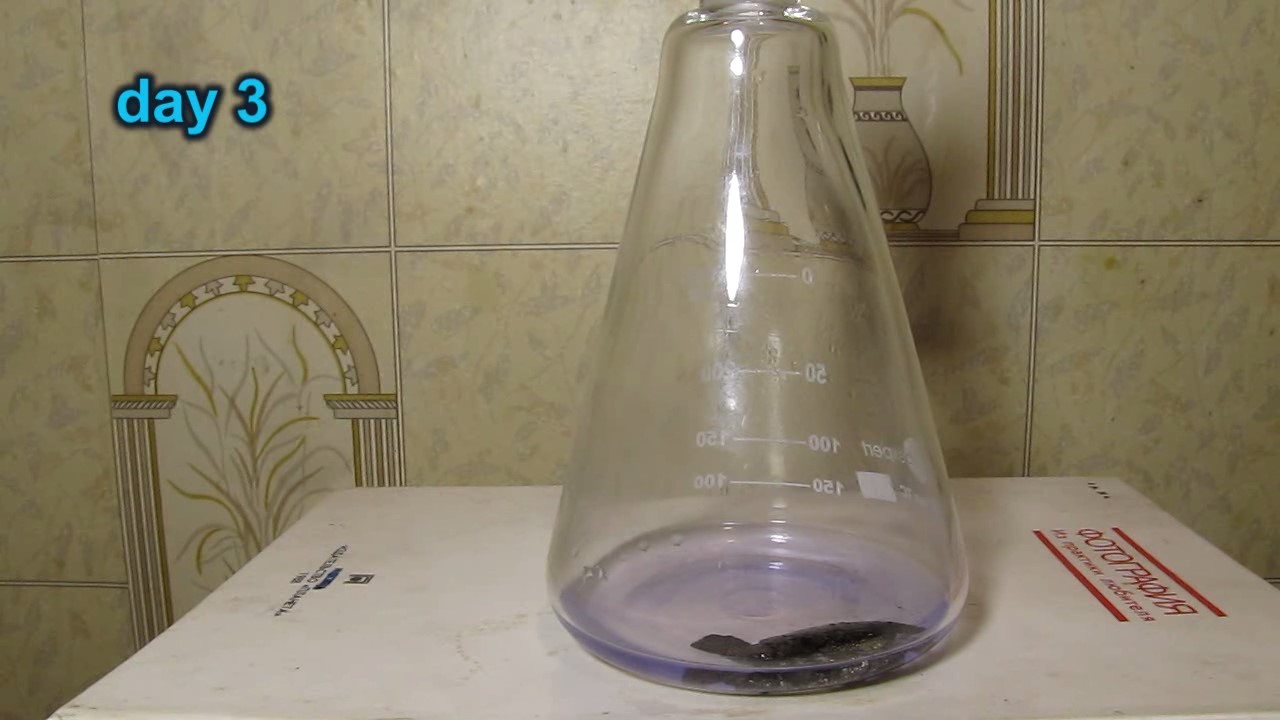
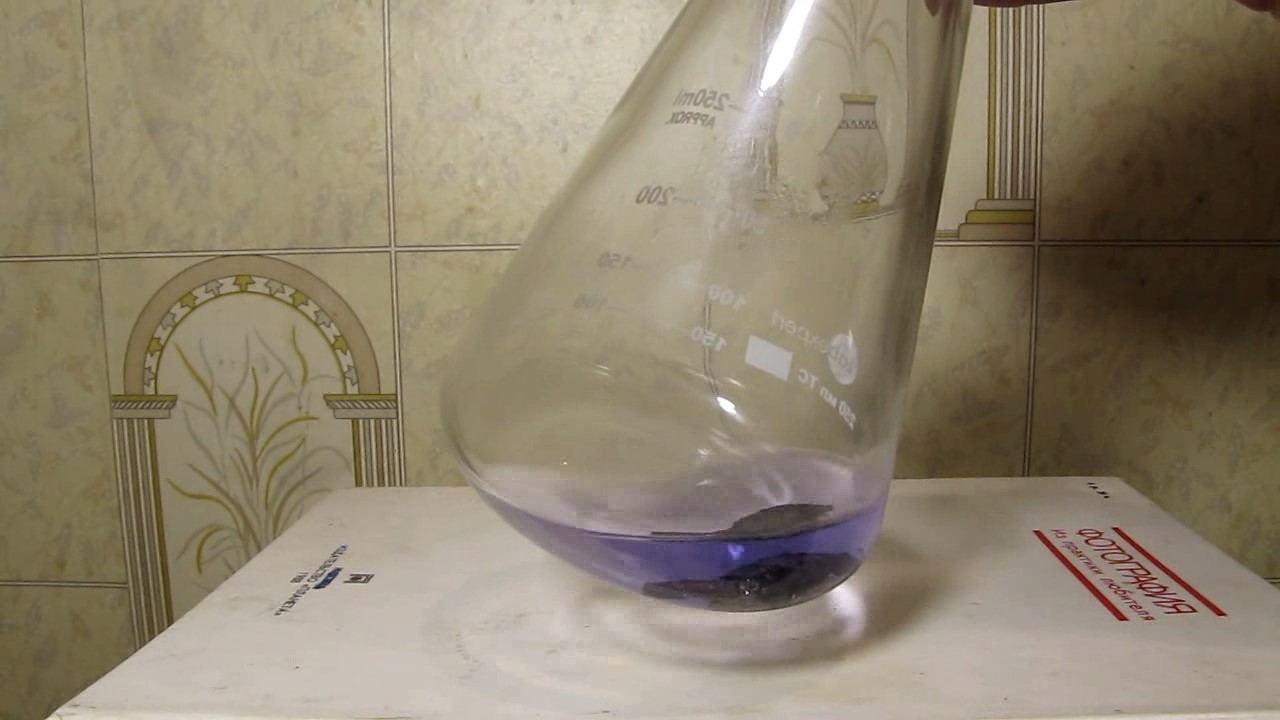
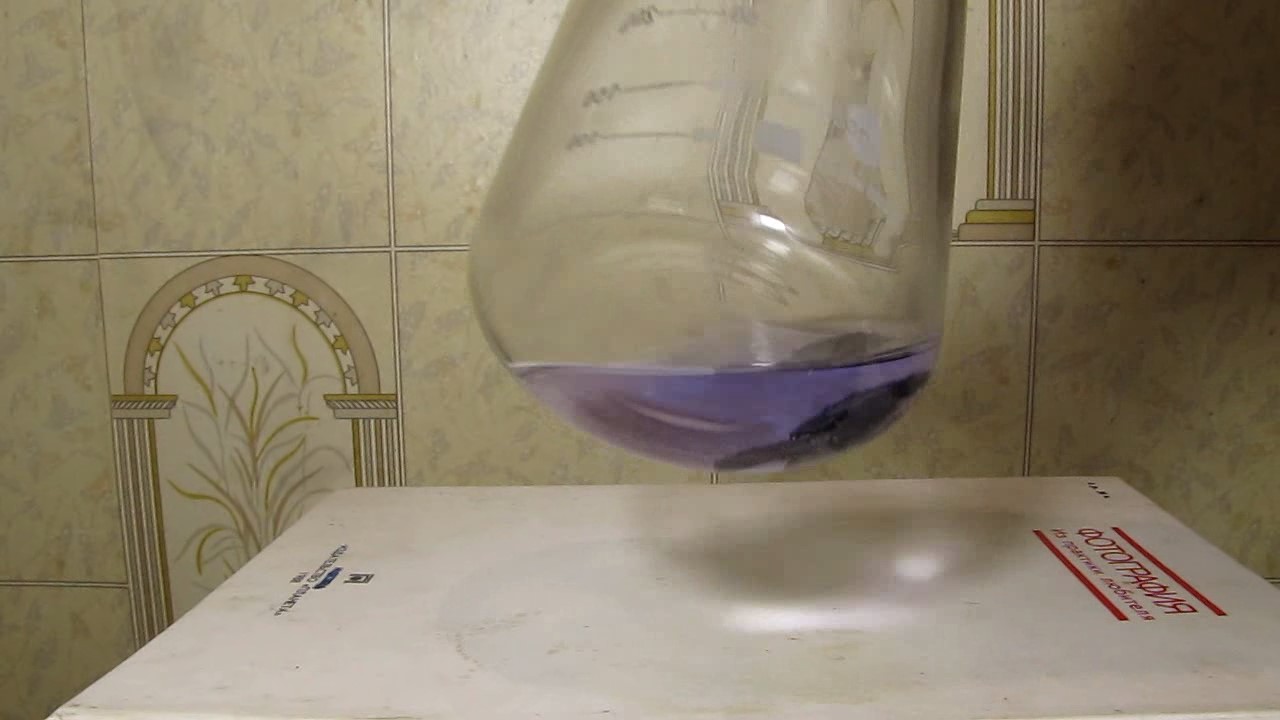
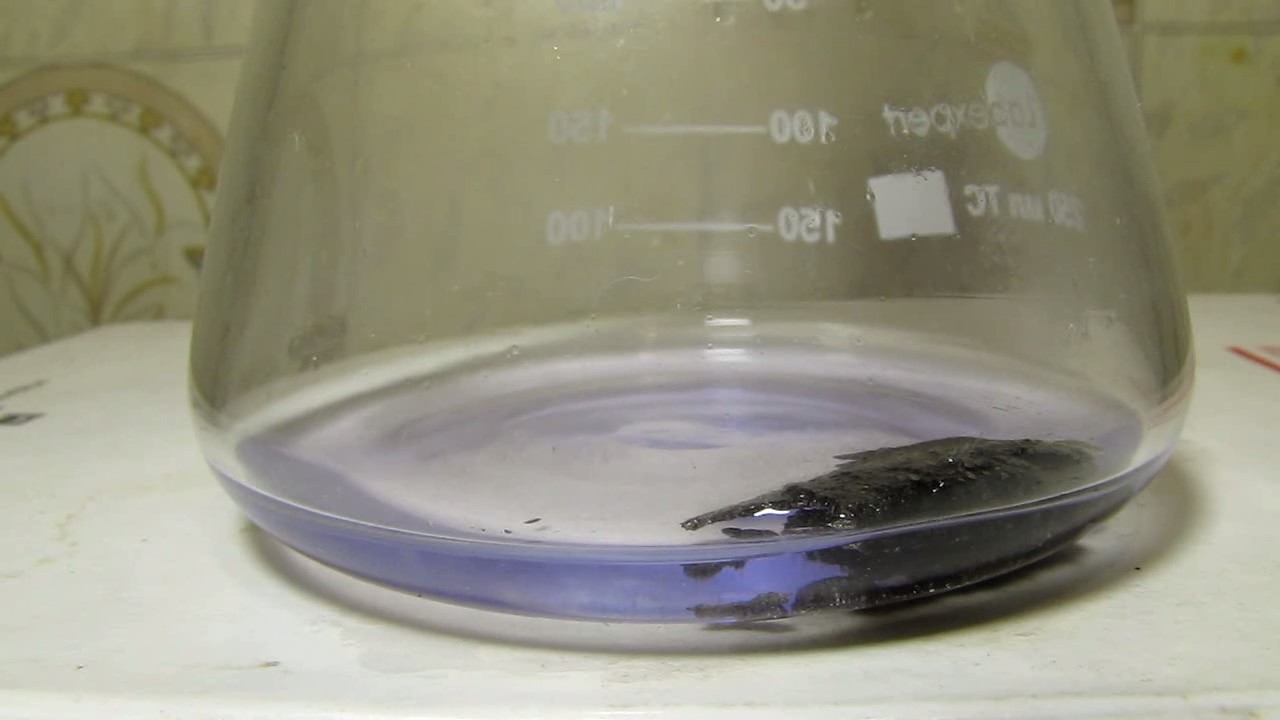
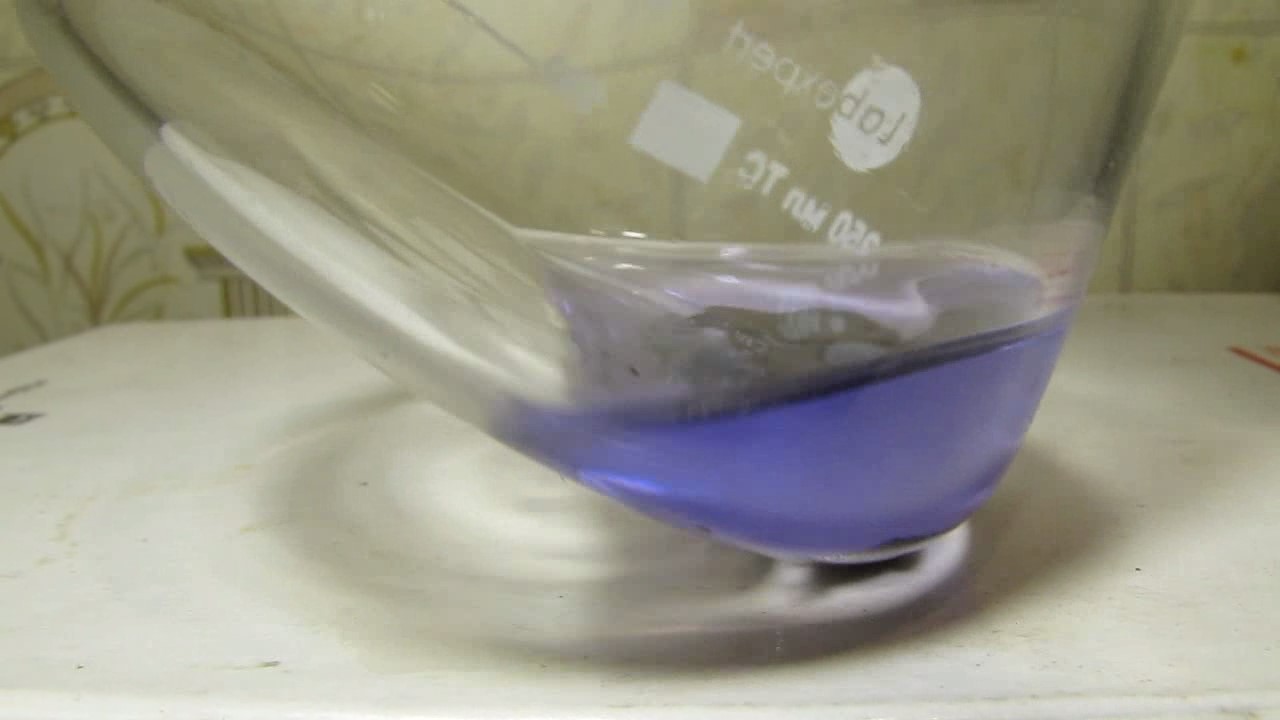
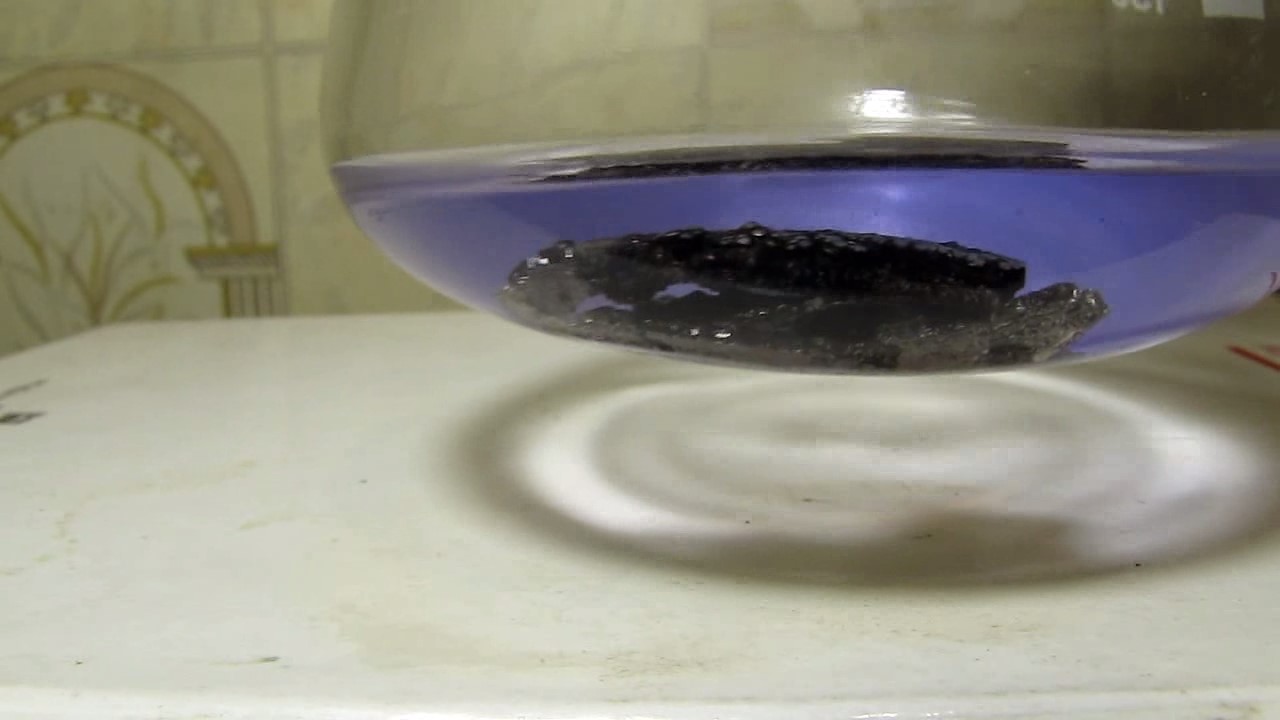
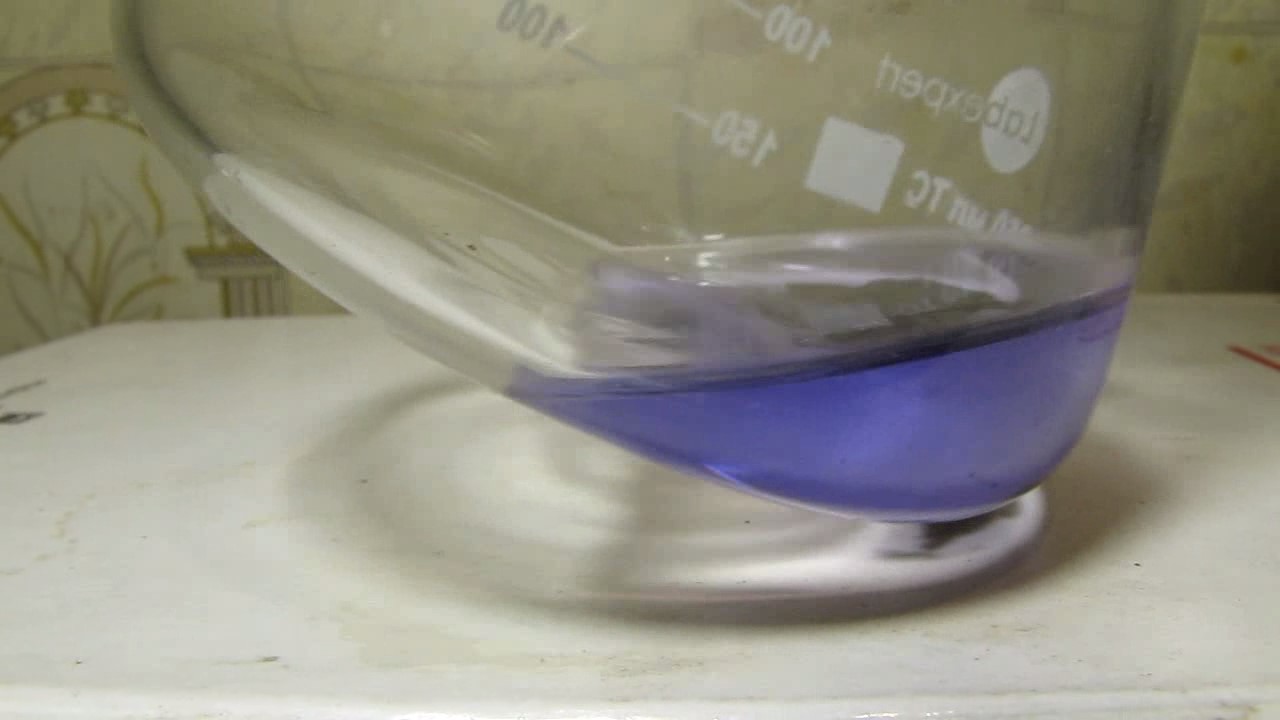
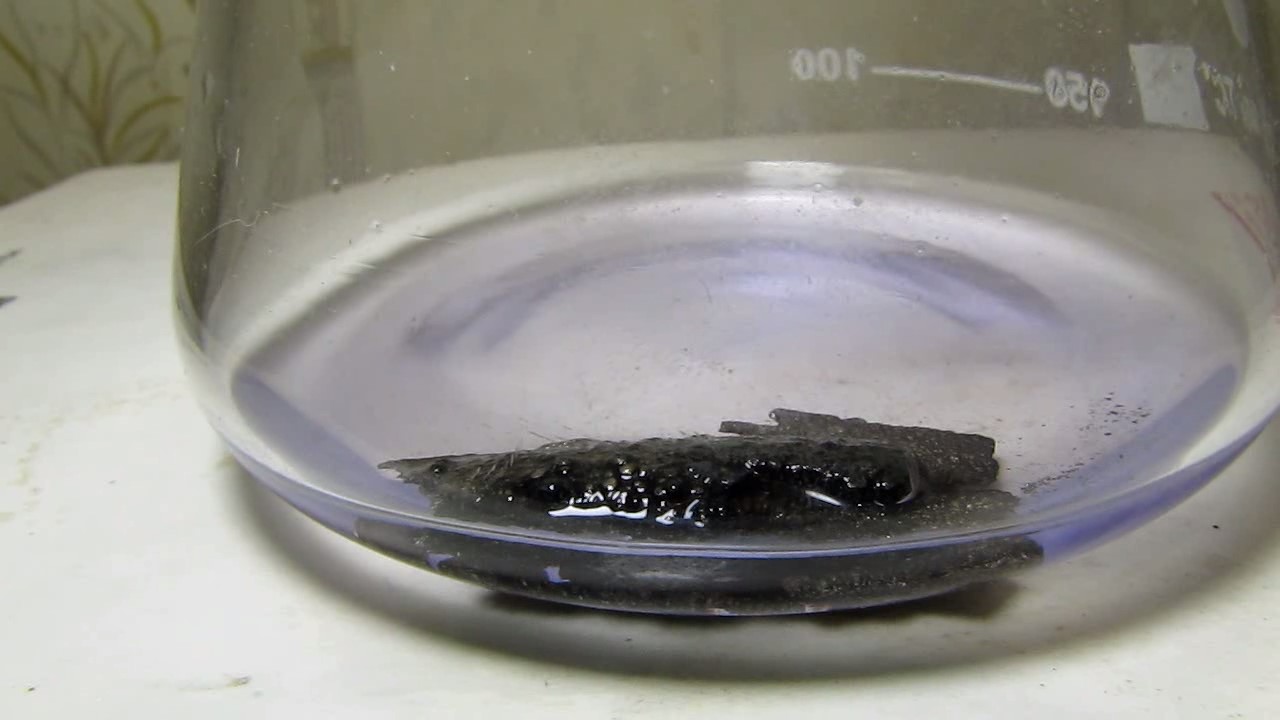
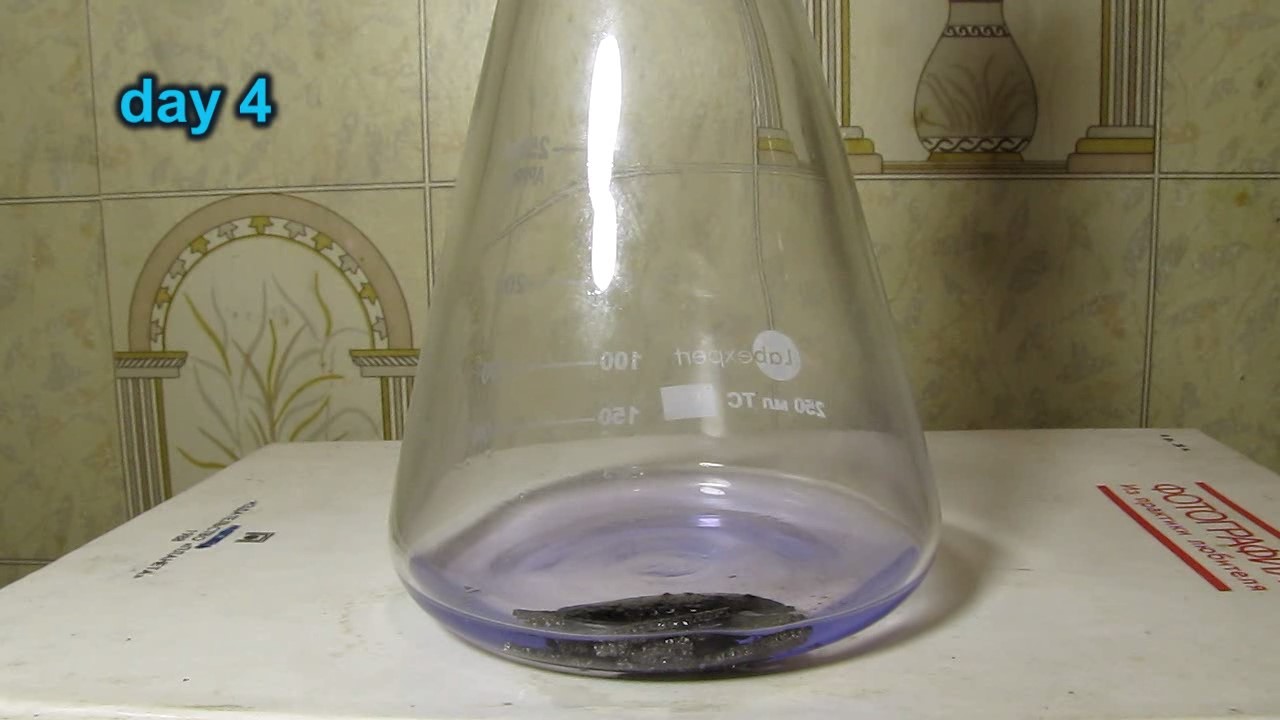
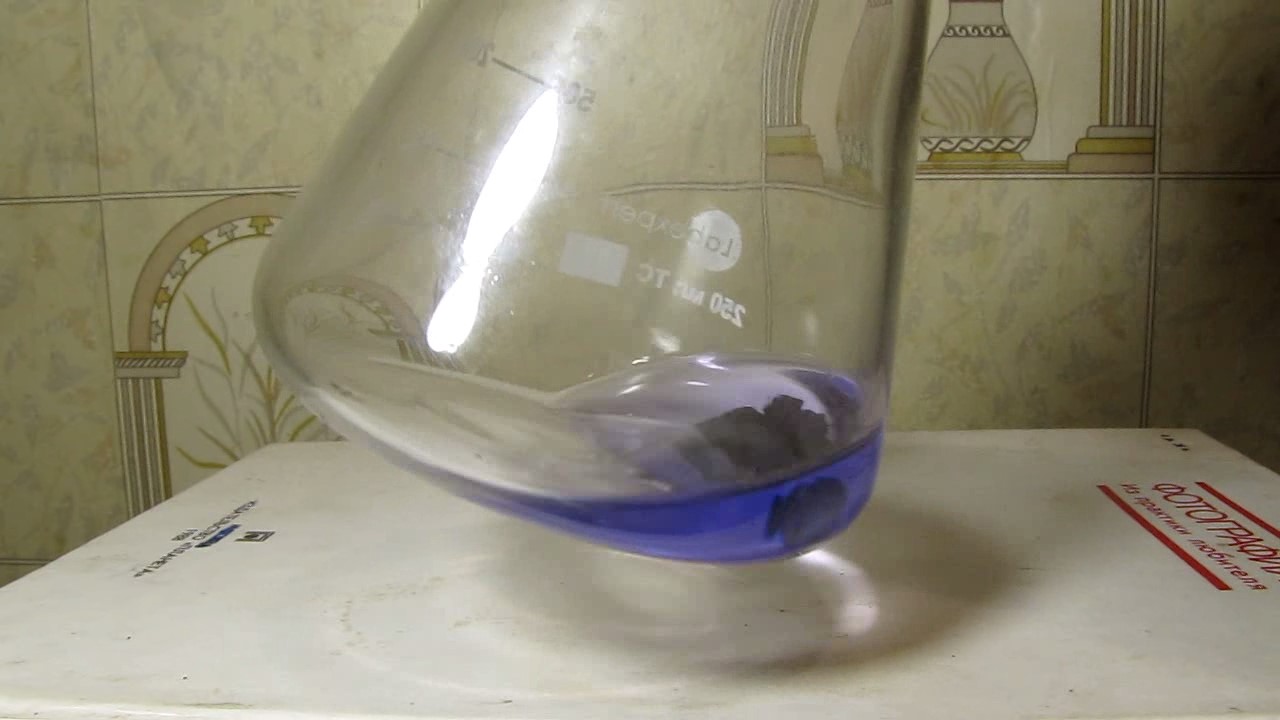
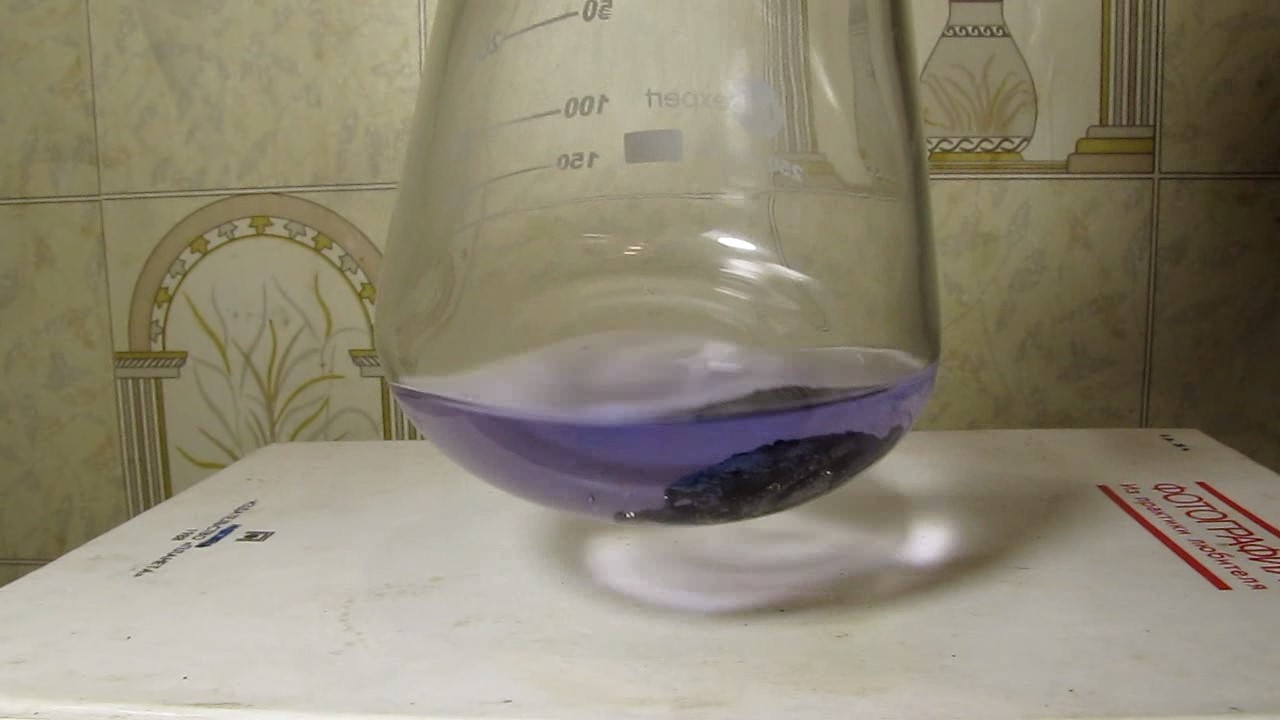
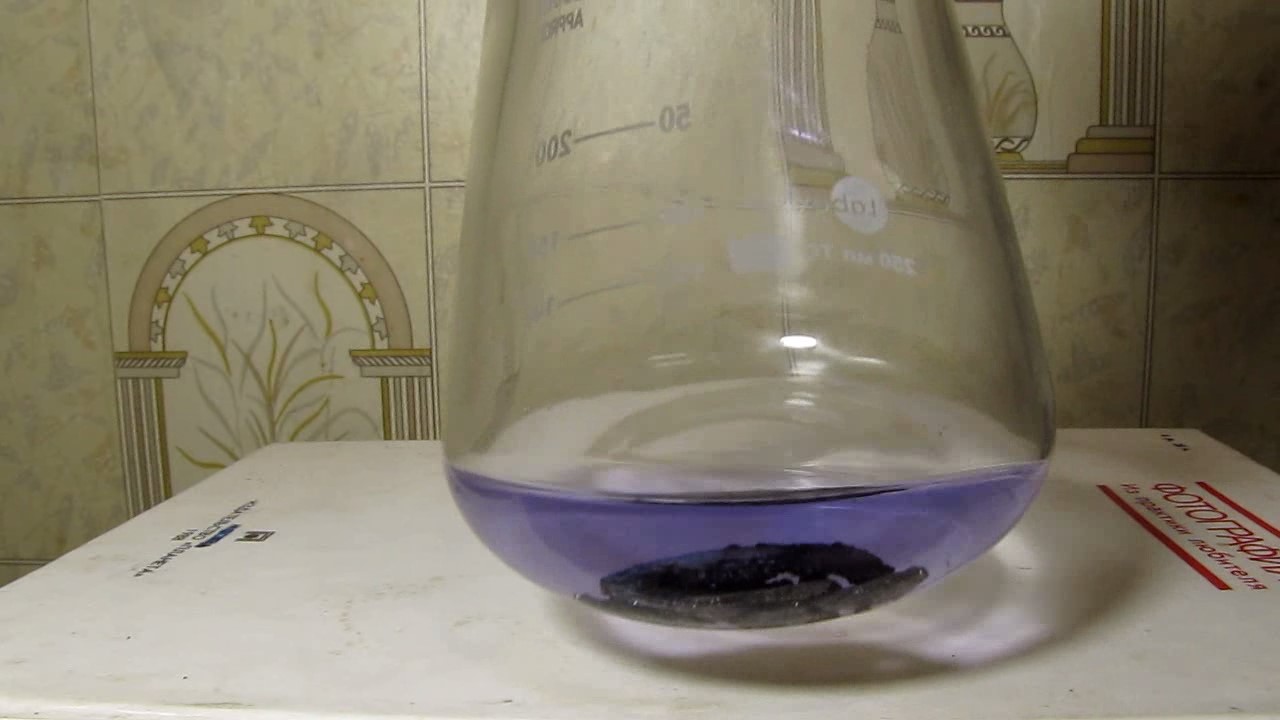
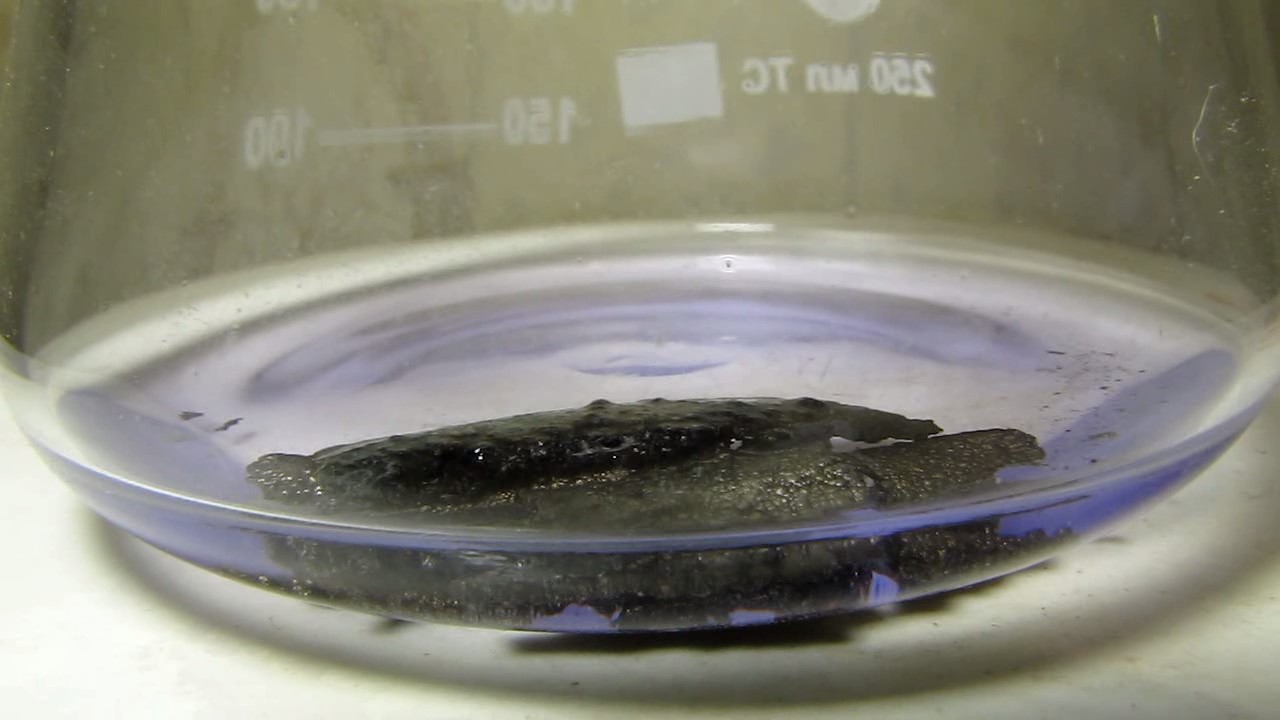
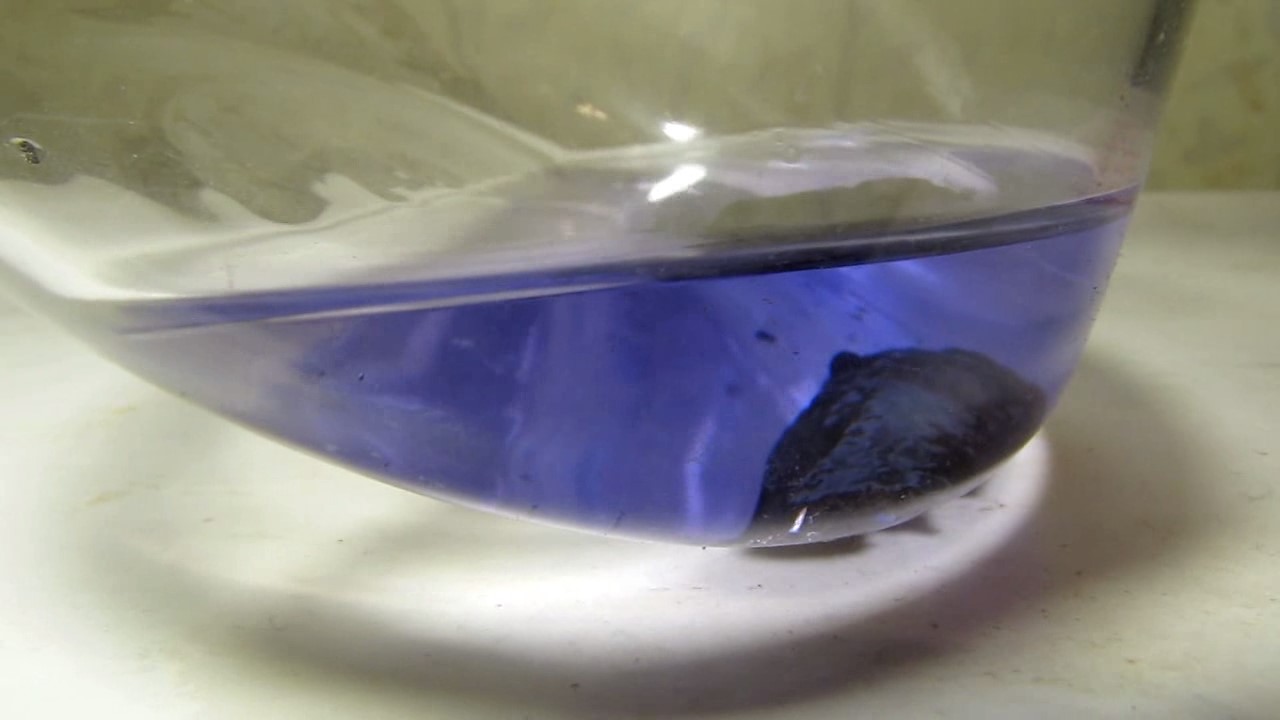
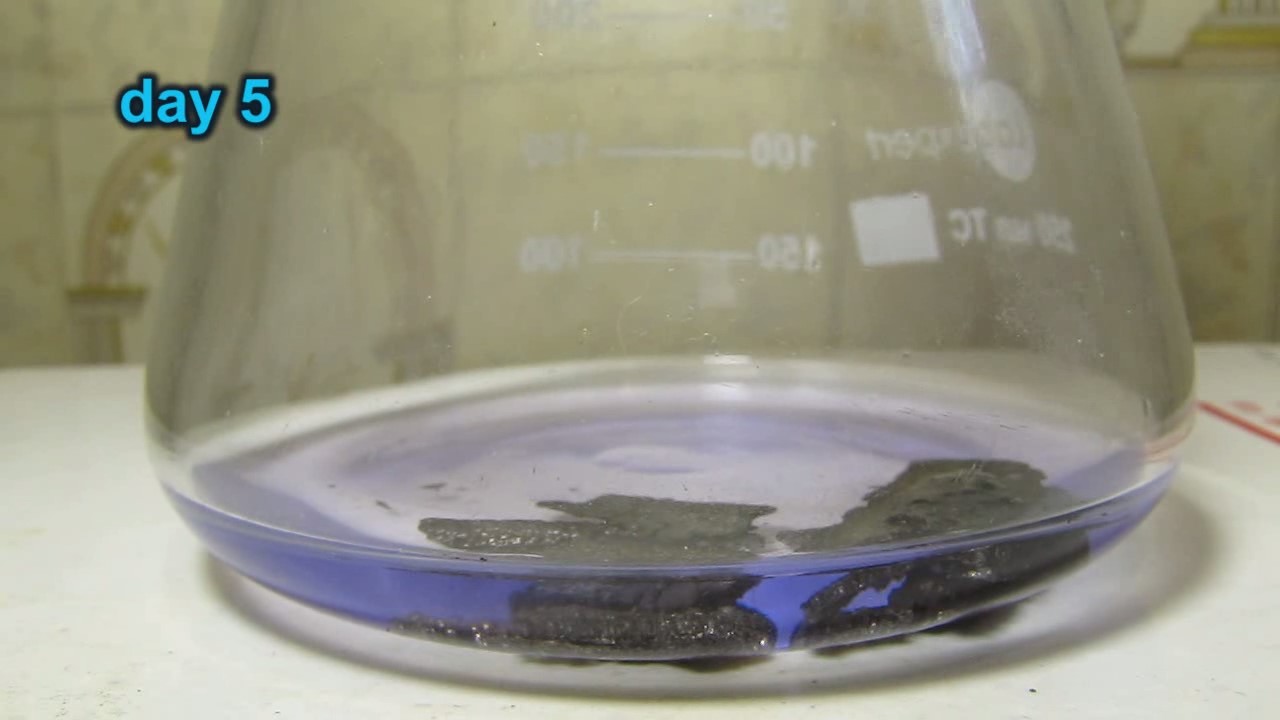
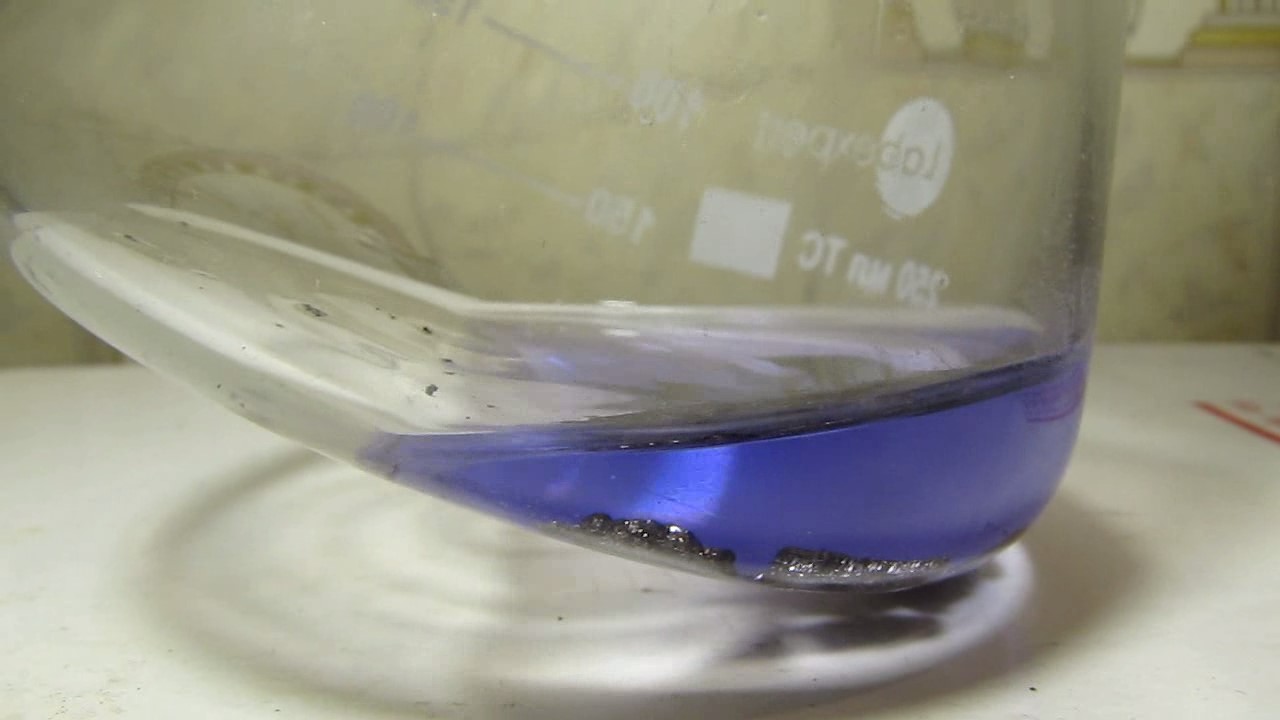
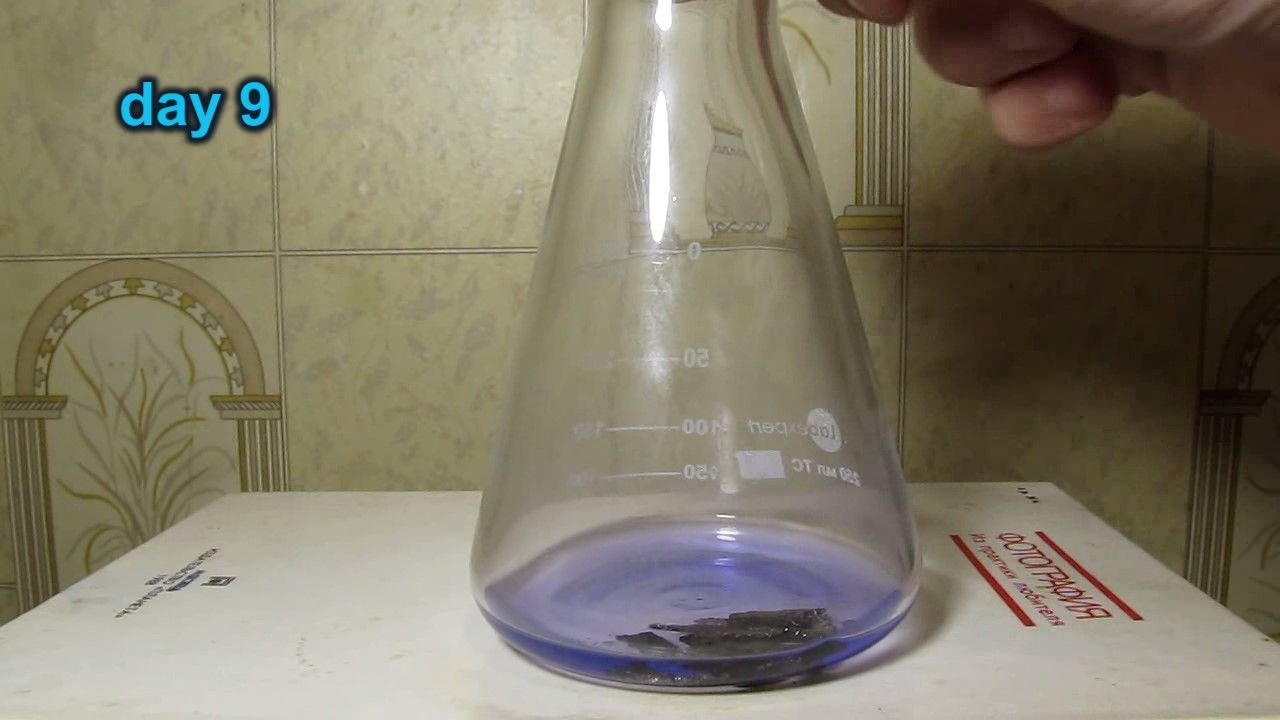
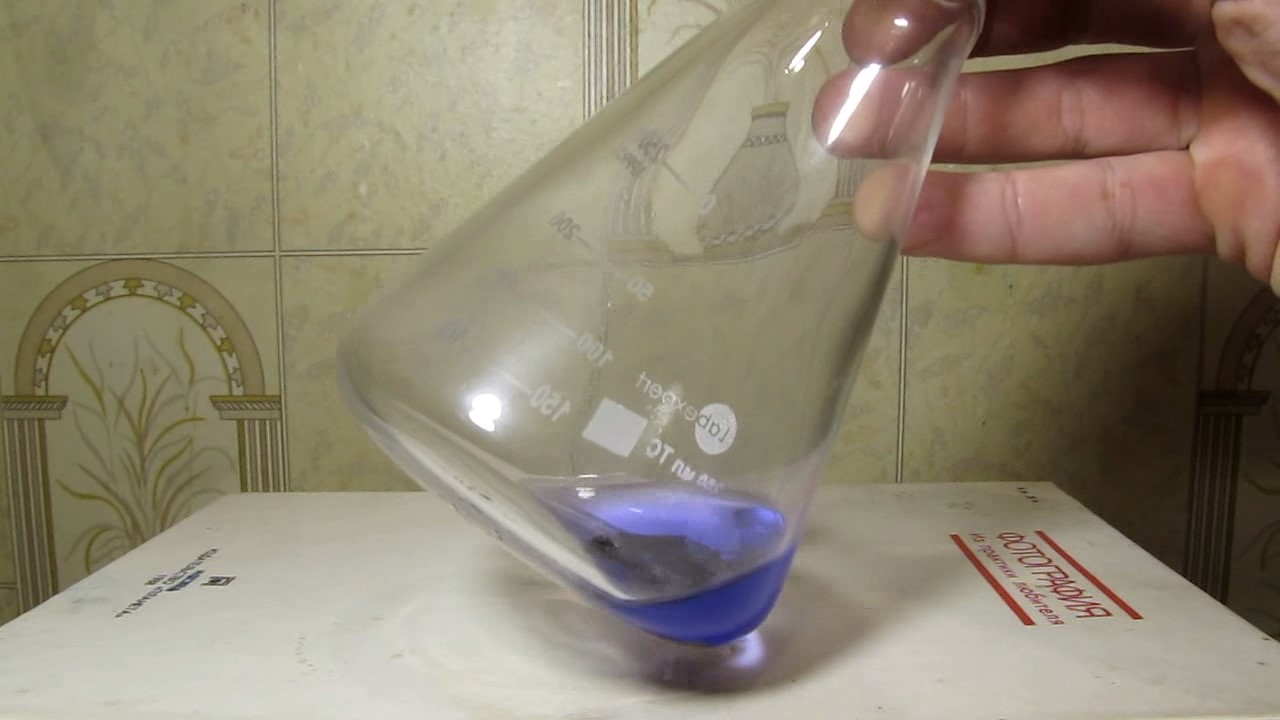
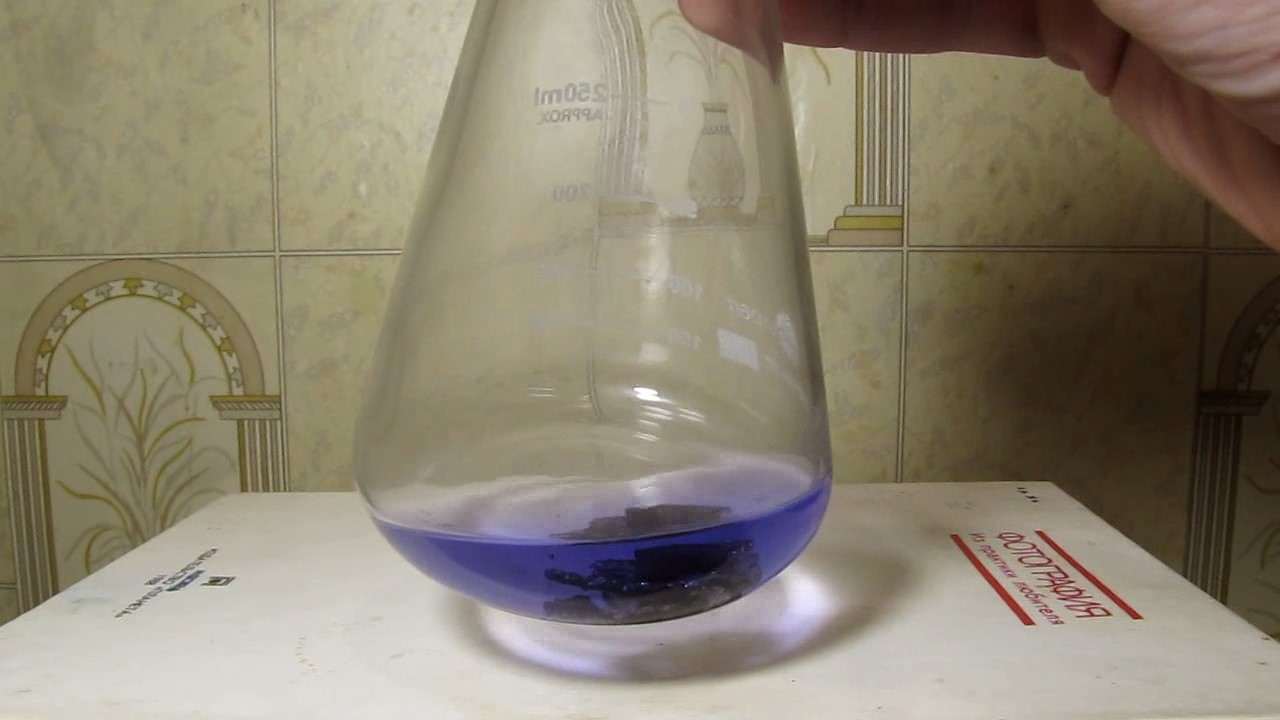
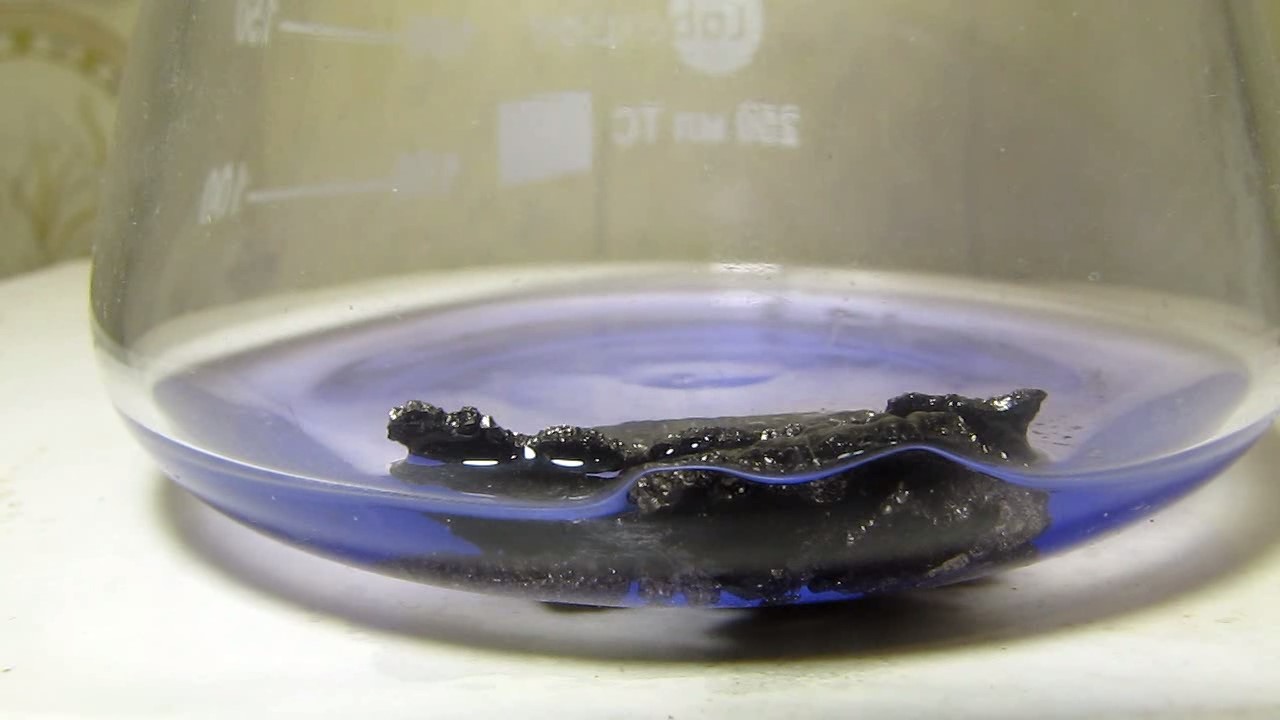
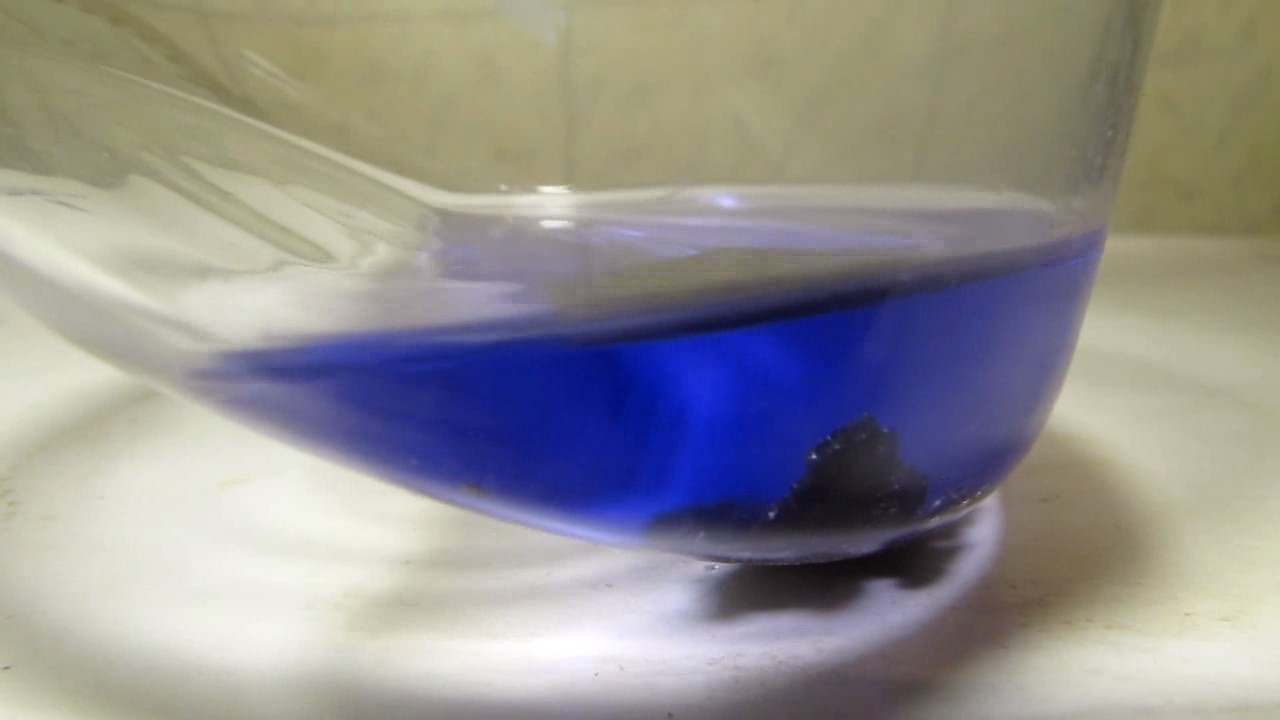
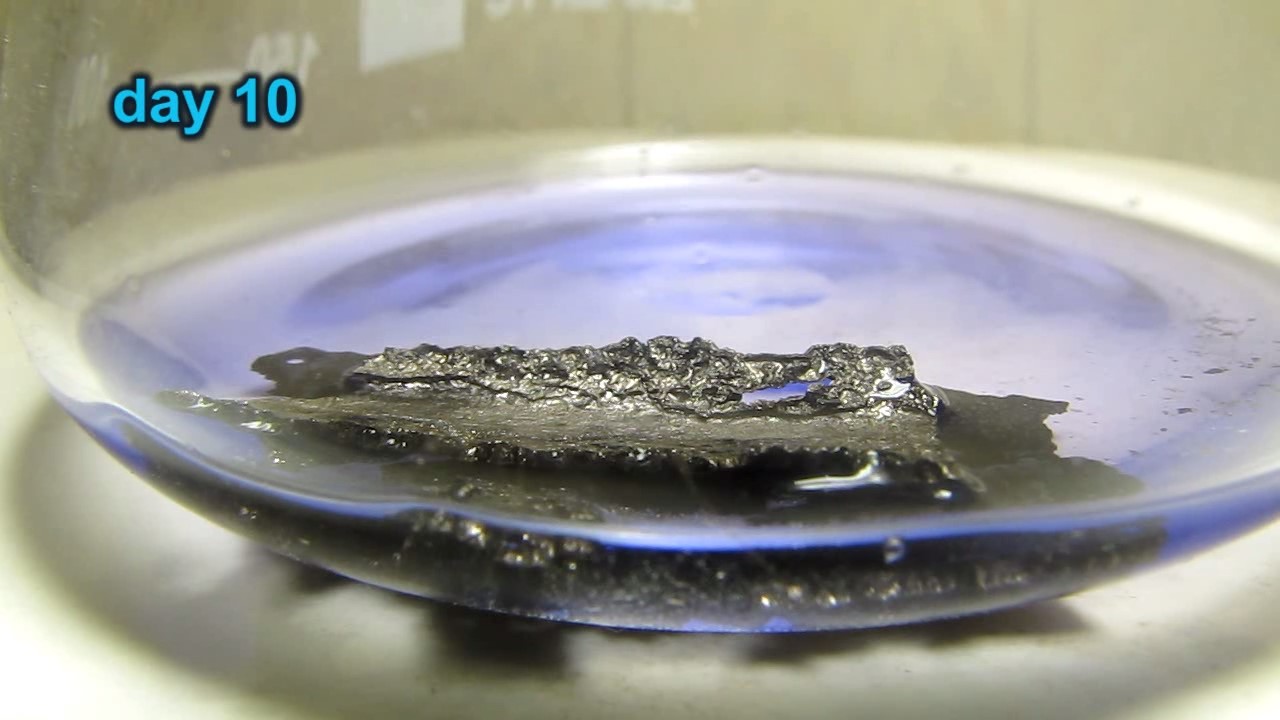
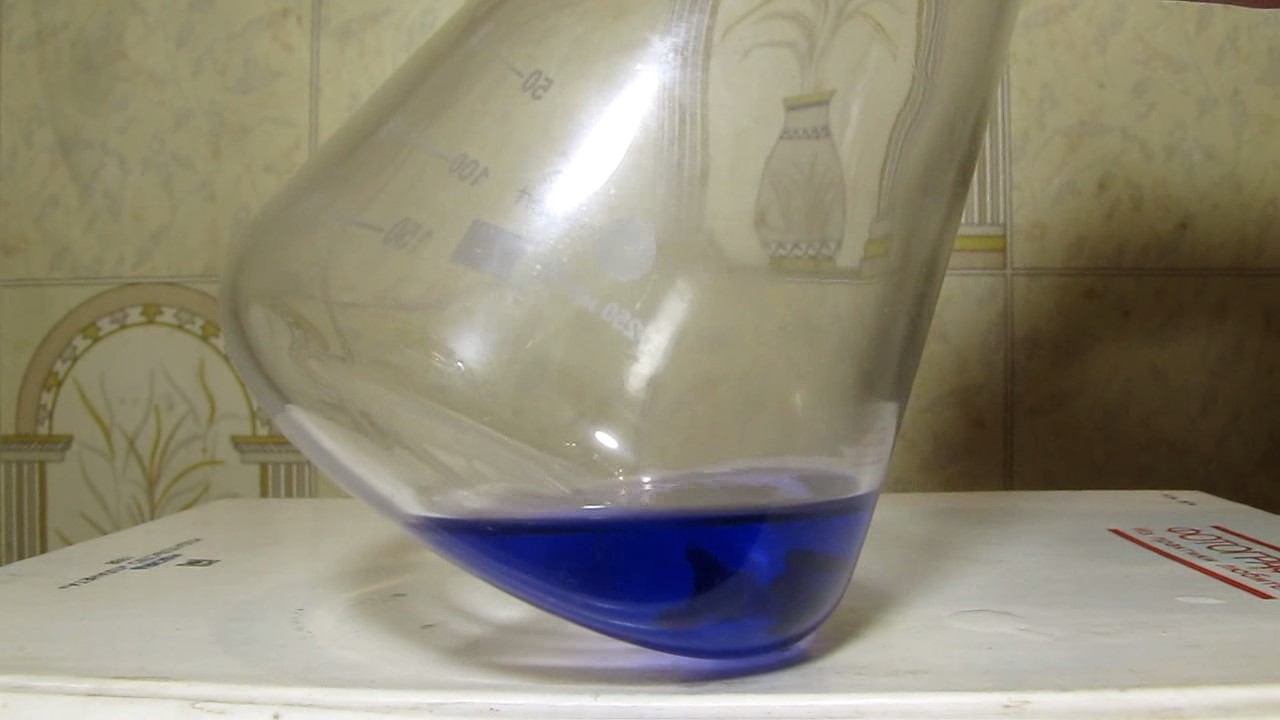
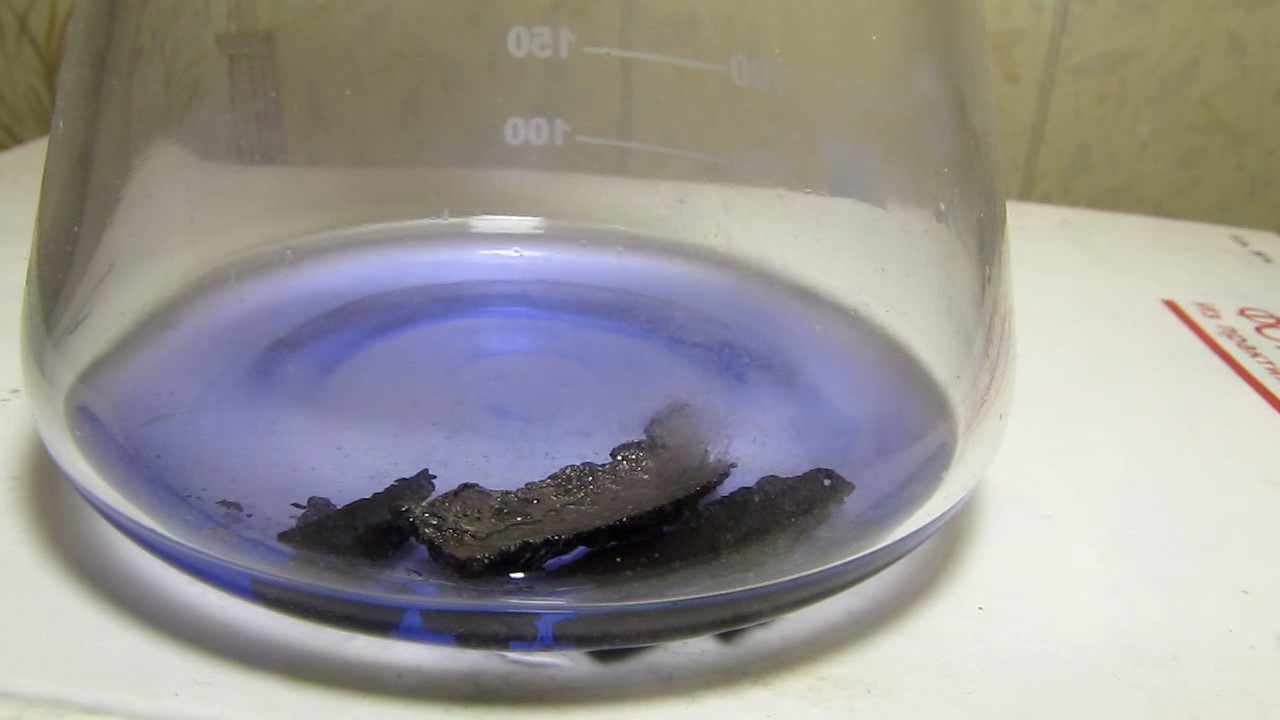
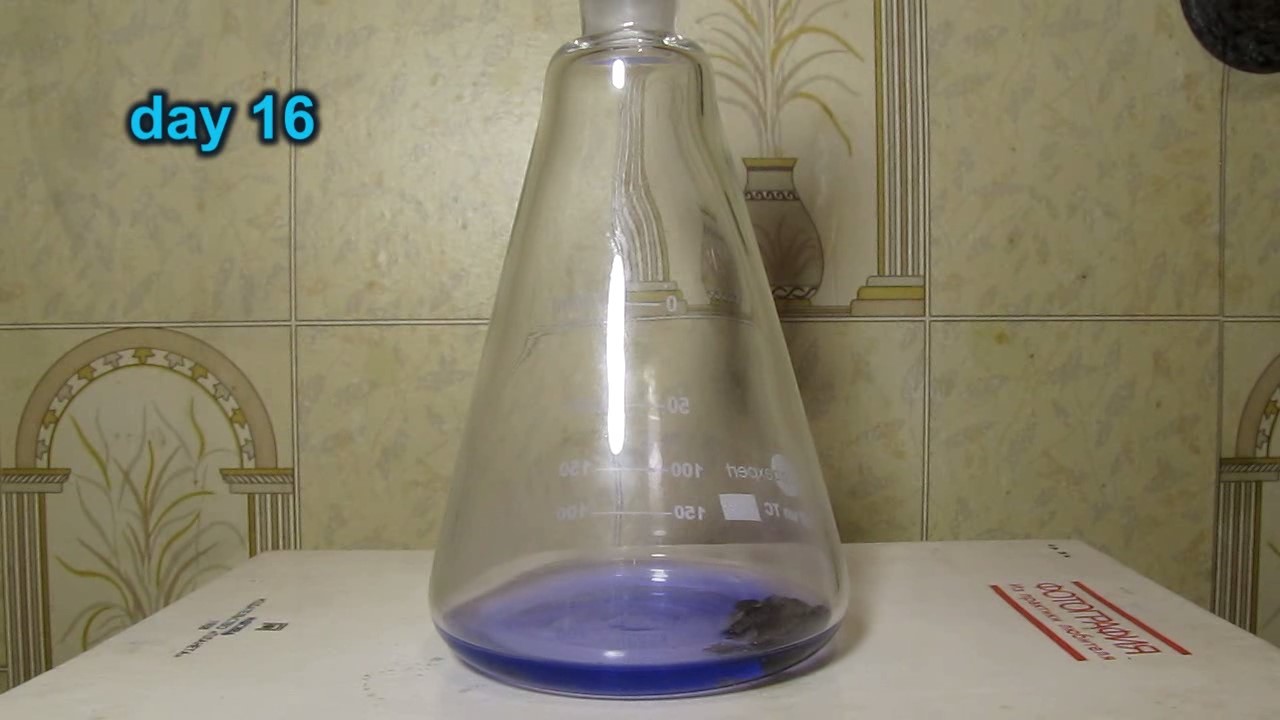
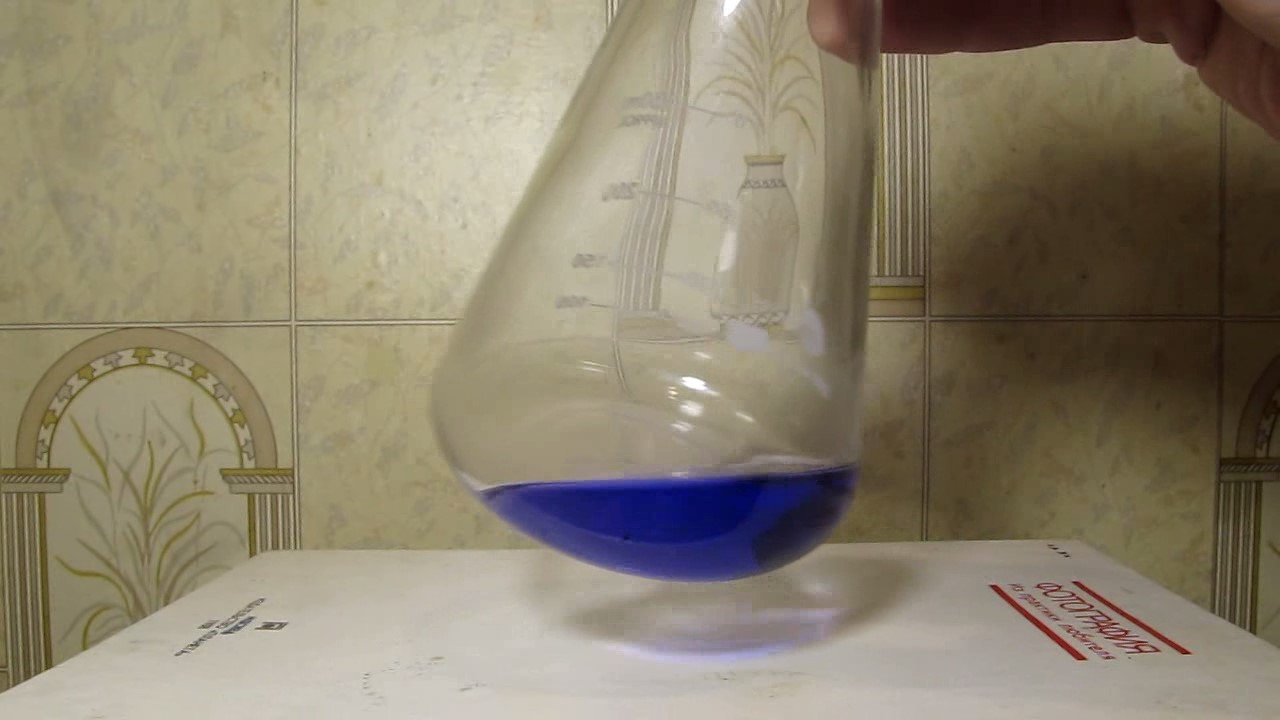
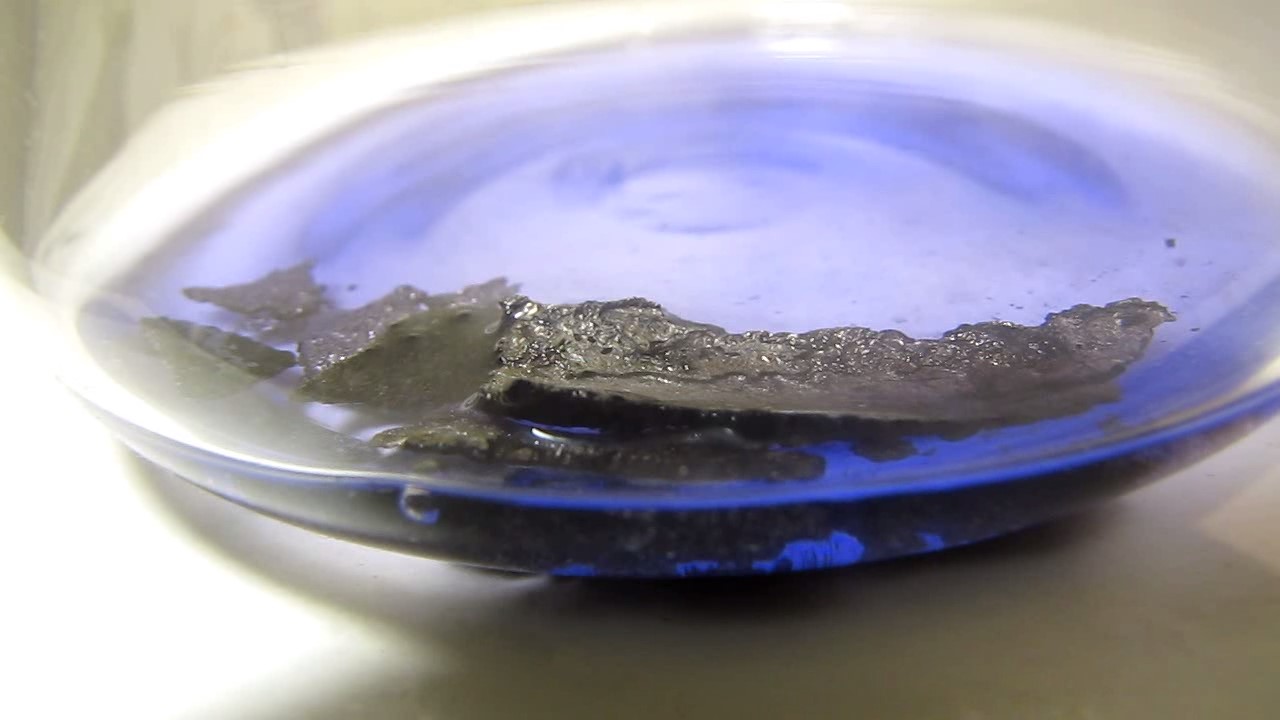
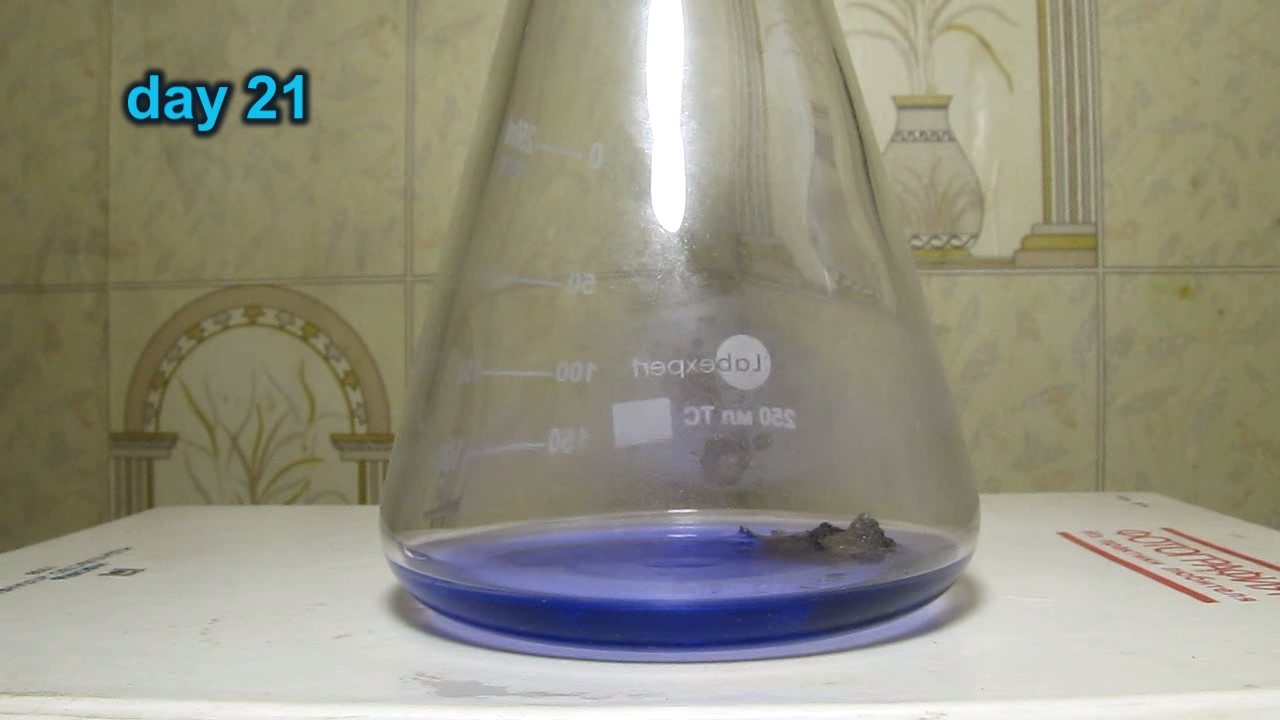
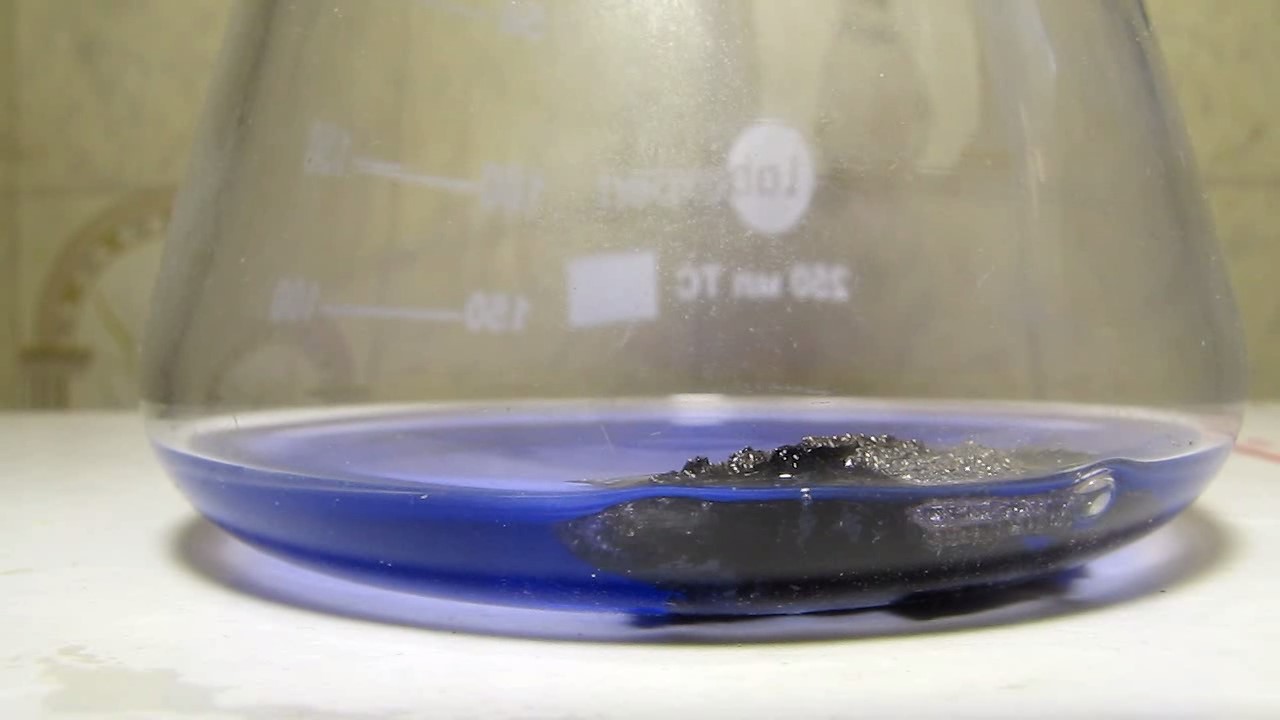
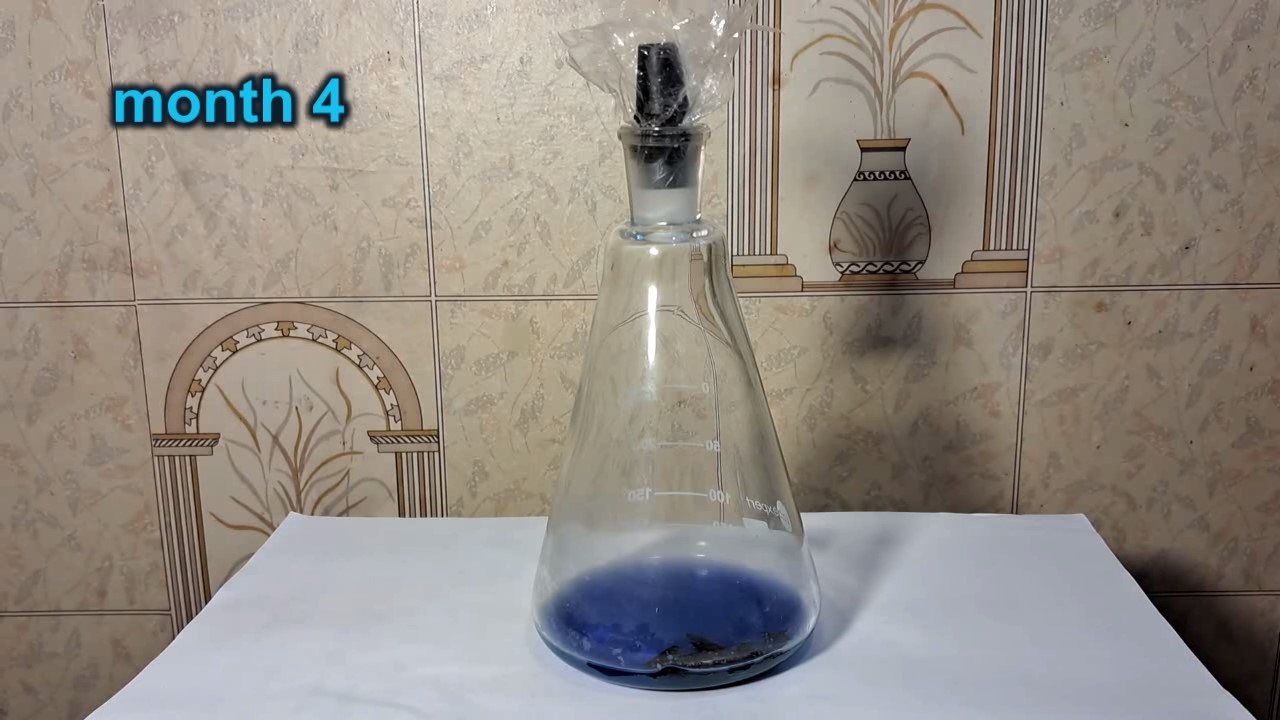
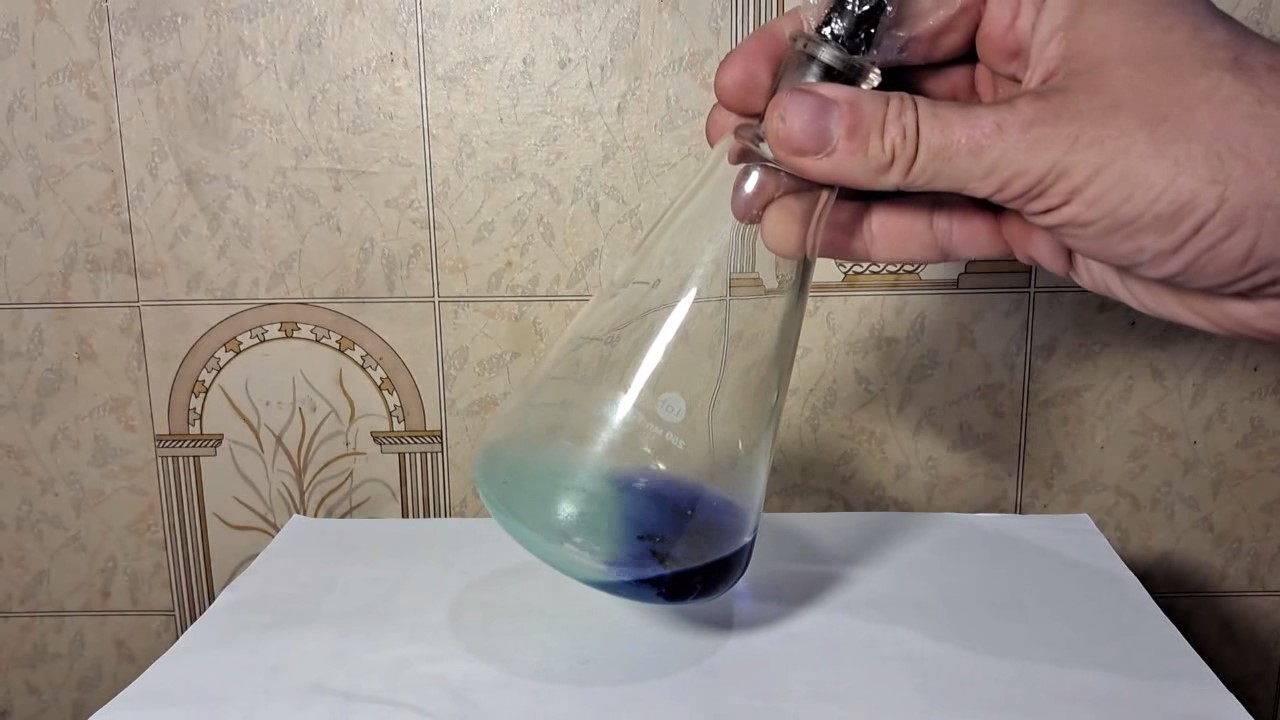
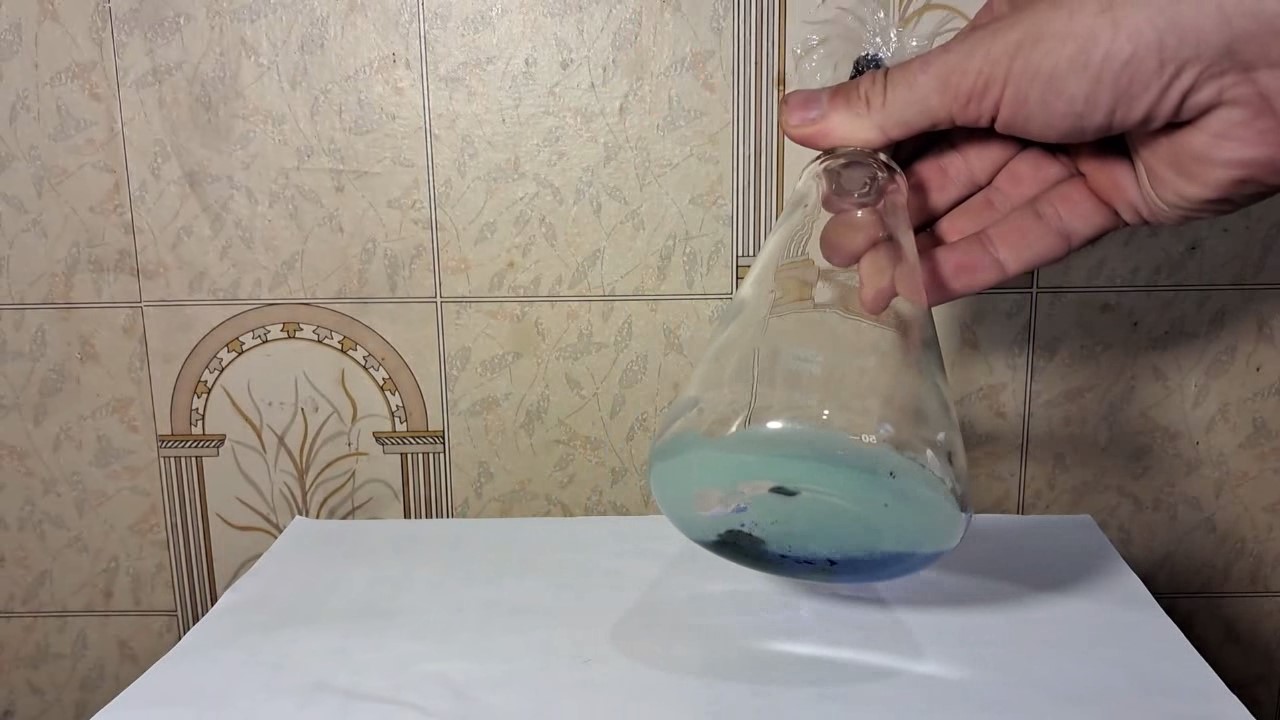
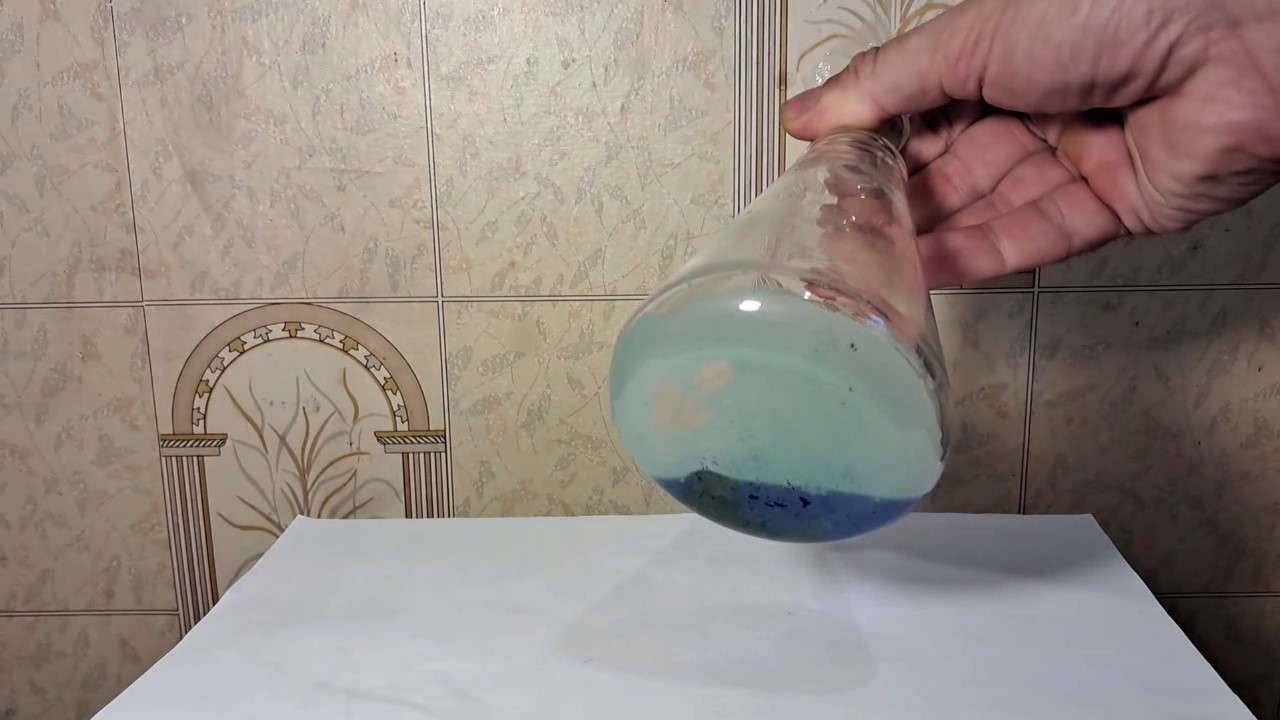
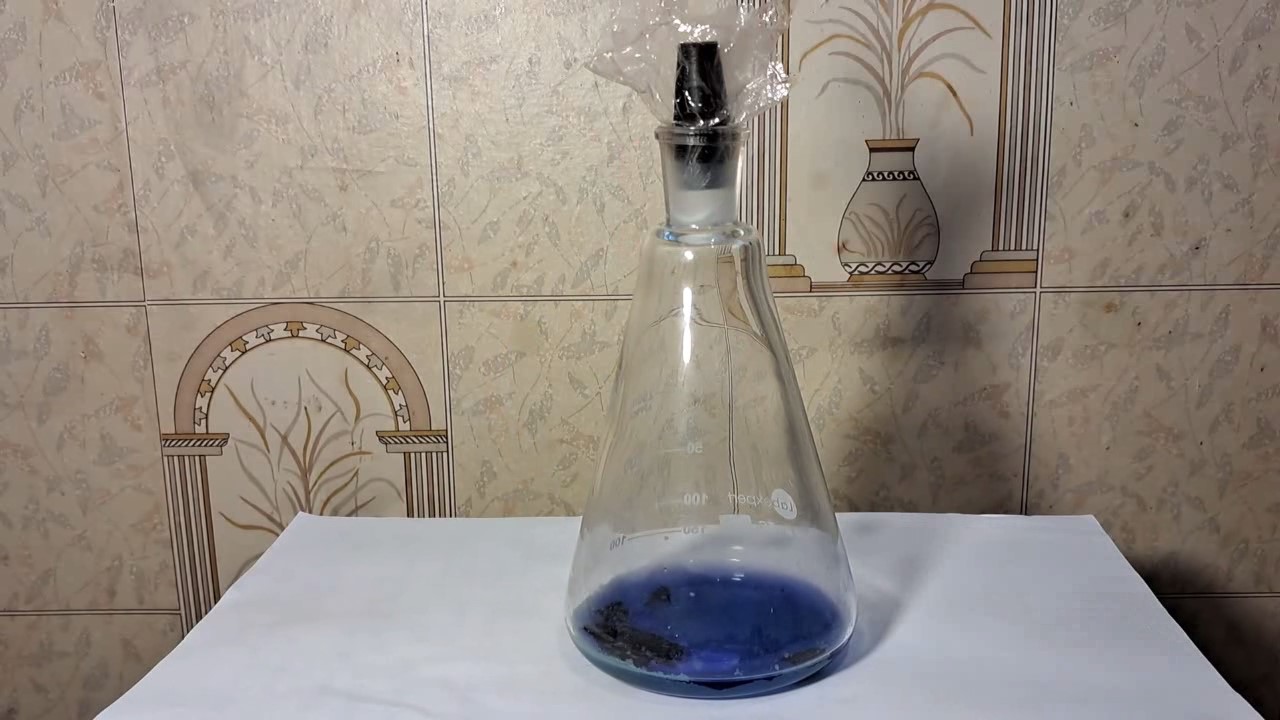
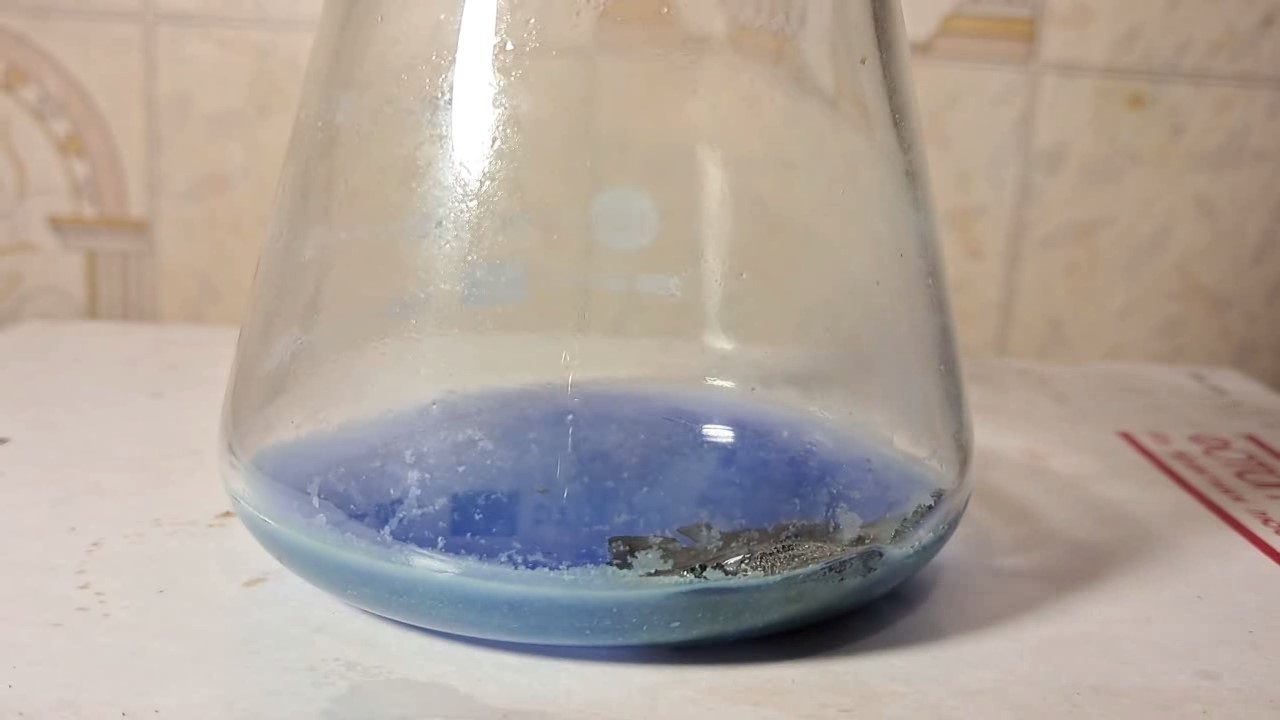
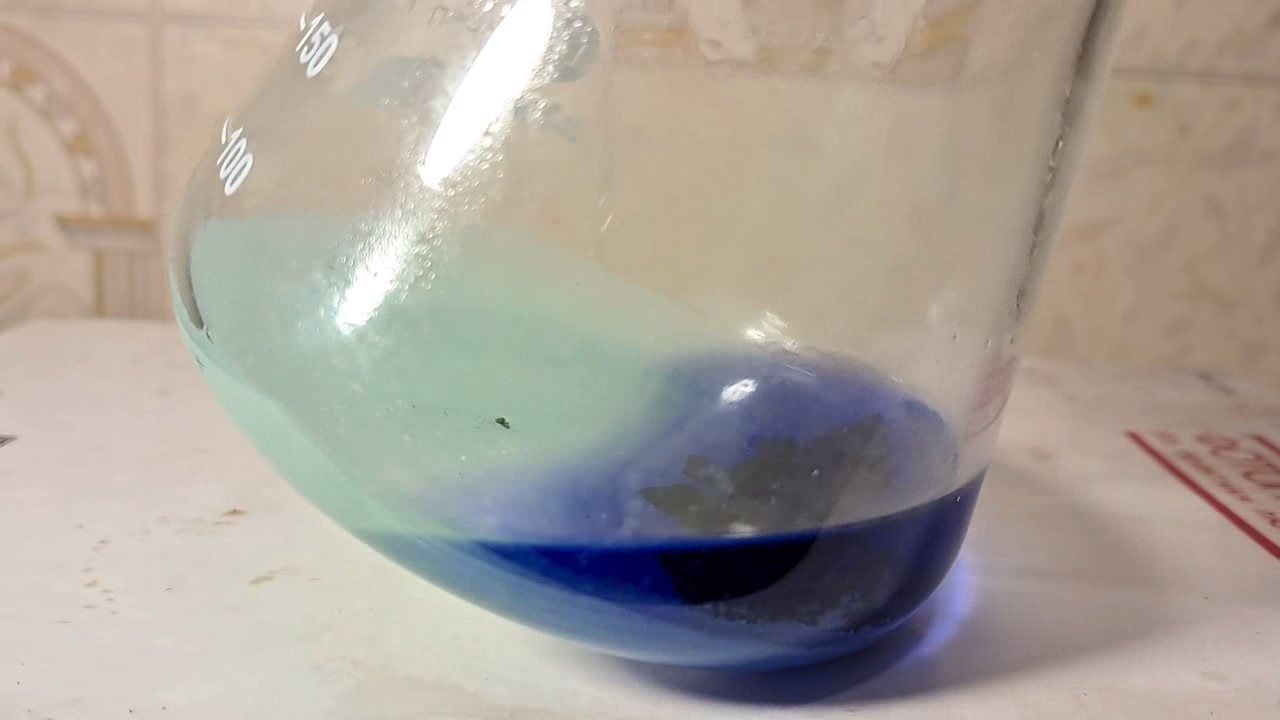
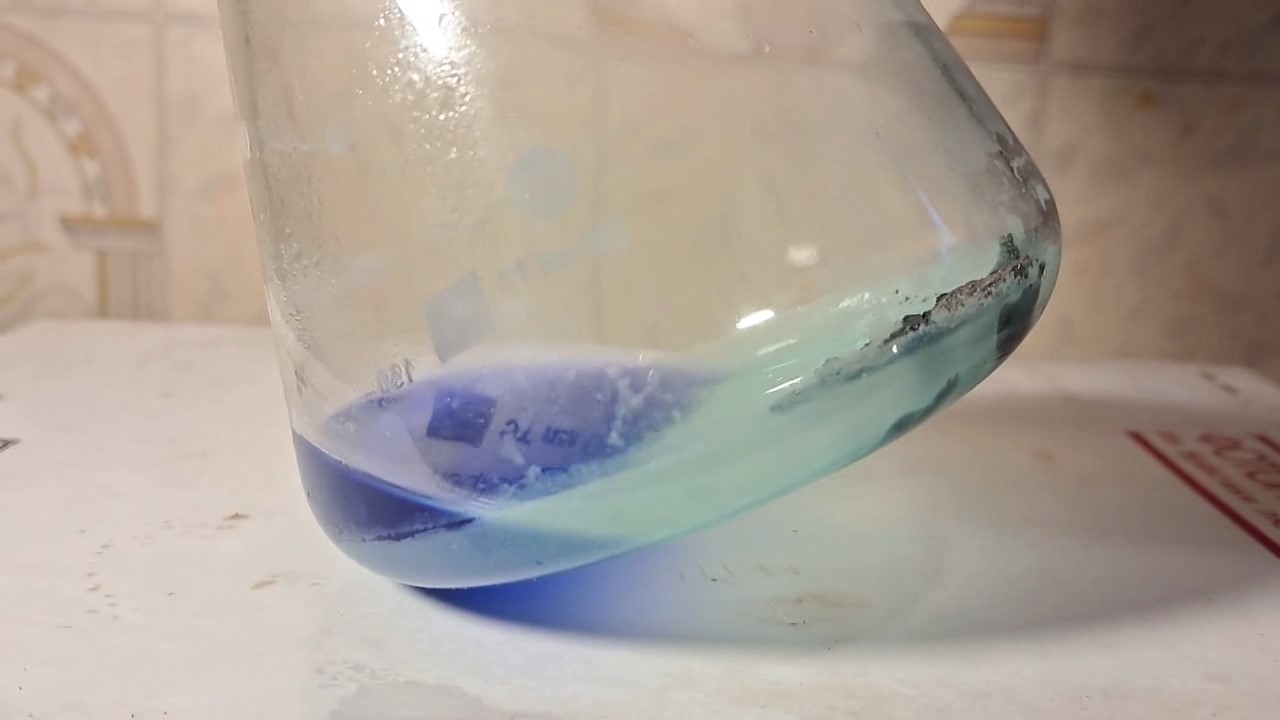
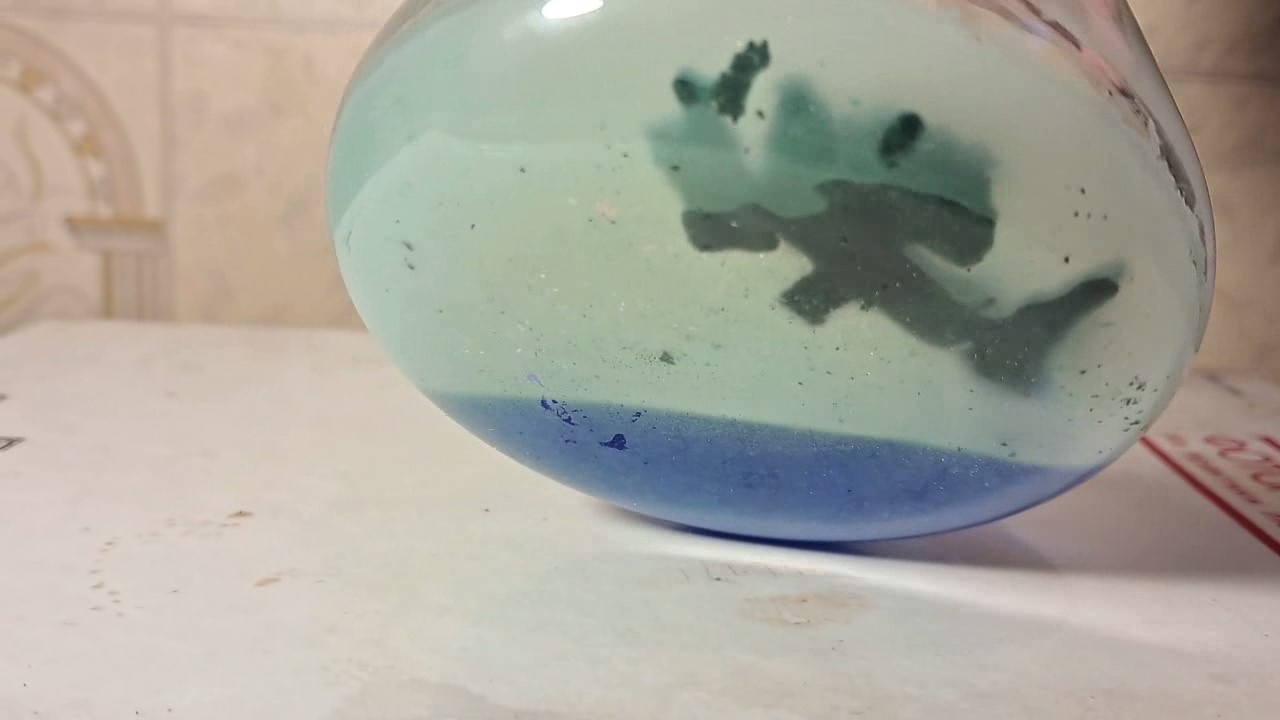
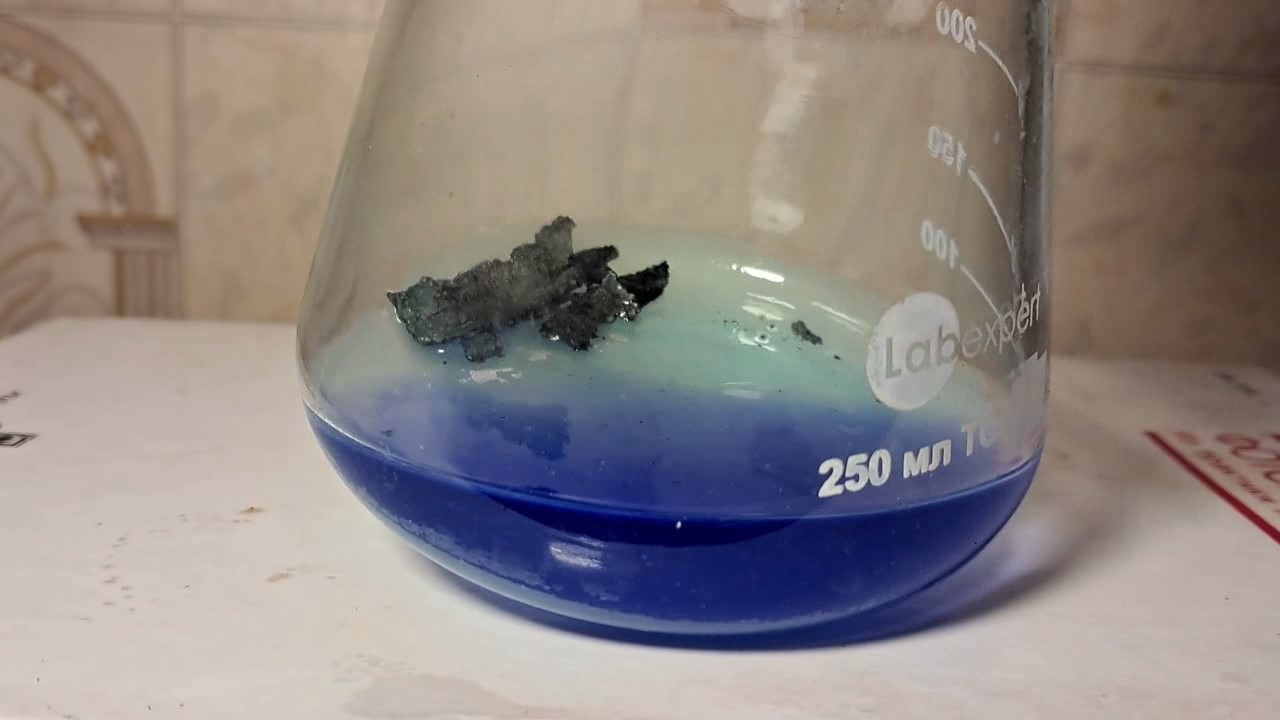
When I attempted a similar experiment with zinc, the color of the solution did not change, as the analogous zinc complex [Zn(NH3)4]2+ is colorless. However, the mass of the zinc granules decreased, and after the solution evaporated, a white solid residue was formed [2]. Nickel is another commonly available metal that forms a strong complex with ammonia, [Ni(NH3)4]2+. Unlike zinc, and similar to copper, the nickel-ammonia complex is intensely colored (it is violet or blue-violet). This led me to conduct a similar experiment using metallic nickel. I had metallic nickel sample, specifically pieces of anodes used for the electrochemical nickel plating of steel or copper. When searching through my metal collection, I found another nickel sample. This was an "electroless nickel" (the nickel precipitated by electroless nickel plating, ENP). In most cases, nickel coatings are applied to metals using electric current, but an alternative method involves the reduction of nickel salts using hypophosphite in an aqueous solution. This process deposits nickel, containing several percent phosphorus (ranging from 2 to 14%), resulting in a nickel-phosphorus alloy (sometimes called "nickel phosphide"). For simplicity, I will refer to this alloy as "nickel." Ideally, the nickel deposits exclusively on the surface of the coated item. However, in practice, it also deposits on the surface of heaters and, to a lesser extent, on the walls of the bath. This unwanted nickel is typically removed by dissolving it in nitric acid (after the bath is stopped and the solution is discarded). The nickel that precipitates on the heaters is mechanically removed and discarded. The samples of this nickel were taken from my previous workplace at an electroplating plant. I weighed several pieces of nickel and placed them in a flask. I then added 20 mL of concentrated ammonia solution and sealed the flask tightly with a stopper. The flask contained a significant amount of air between the stopper and the solution. I periodically shook the flask and occasionally opened it briefly to allow fresh air inside. Here are my observations: 0 hours (start): * The solution was colorless, and the metal appeared silvery-white. 19 hours: * The solution turned light purple, and the surface of the metal began to darken. Day 2: * The color of the solution became more intense. Most of the nickel surface turned black. Day 3: * The solution's color deepened. Most of the nickel surface remained black. Day 4: * The solution was dark purple, and most of the nickel surface was black. Days 5 and 6: * No significant change; the observations remained consistent with Day 4. Day 9: * The solution's color became even more intense. Day 10: * The solution grew darker, with most of the nickel surface still black. Days 12 and 16: * No significant change; the solution and nickel surface remained the same. Day 21: * The solution was a dark purple, almost opaque, with most of the nickel surface black. Month 4: * The solution remained dark purple. Nearly the entire nickel surface was black, and the bottom and lower areas of the flask walls were coated with a green substance. __________________________________________________ 1 See the set of articles: Copper, Silver, Gold, Platinum Metals [link]. 2 See the article: Zinc, ammonia and air (reaction of zinc metal with aqueous ammonia and oxygen) [link]. |
|
Растворение никеля в водном растворе аммиака
Как известно, металлическая медь реагирует с водным раствором аммиака в присутствии воздуха. В результате металл окисляется и переходит в раствор в виде комплекса [Cu(NH3)4]2+ [1]. Бесцветный раствор окрашивается в интенсивно-синий цвет. Аналогично ведут себя сплавы меди, например, латунь.
Когда я попробовал провести такой эксперимент с цинком, то цвет раствора не изменился, поскольку аналогичный комплекс цинка [Zn(NH3)4]2+ бесцветен. Однако, масса гранул металла уменьшилась, а после упаривания раствора образовался белый твердый остаток [2]. Никель - еще один общедоступный металл, который образует прочный комплекс с аммиаком [Ni(NH3)4]2+. В отличие от цинка и аналогично меди, комплекс никеля с аммиаком интенсивно окрашен (он имеет фиолетовый или сине-фиолетовый цвет). Возникла очевидная идея провести аналогичный эксперимент с металлическим никелем. Металлический никель у меня был - куски анодов, которые использовались для электрохимического покрытия никелем стали или меди. Когда взял ящик с моей коллекцией металлов и стал искать никель, то обнаружил еще один образец данного металла. Это был т.н. "химический никель" (никель, полученный методом electroless nickel plating, ENP - "безтоковое нанесение никелевого покрытия"). В большинстве случаев никелевое покрытие наносят на металлы с помощью электрического тока, но не всегда. Иногда применяют альтернативный метод, а именно - восстановление солей никеля с помощью гипофосфита в водном растворе. В результате образуется никель, который содержит несколько процентов фосфора (пишут, что 2 до 14%); другими словами, на поверхности покрываемого изделия осаждается сплав никеля и фосфора (иногда его называют также "фосфид никеля"). Для простоты далее мы будем называть этот сплав "никель". В идеальном случае никель осаждается исключительно на поверхности покрываемого изделия. Однако, в реальности никель также осаждается на поверхности нагревателей, в меньшей мере - на стенках ванны. Этот никель приходится удалять. Работу ванны останавливают, рабочий раствор выливают в отходы, затем приставший никель растворяют азотной кислотой. Никель, который отложился на нагревателях, удаляют механически и выкидают в мусор. Именно его и взял домой для экспериментов, когда работал на гальваническом производстве. Взвесил несколько кусочков никеля, поместил их в колбу. Прилил 20 мл концентрированного раствора аммиака, закрыл колбу герметично пробкой. Между пробкой и раствором в колбе было много воздуха. Оставил колбу стоять, периодически встряхивая. Иногда открывал на короткое время пробку, чтобы впустить в колбу новые порции воздуха. Ниже опишу свои наблюдения. 0 часов (начало): * Бесцветный раствор, серебристо-белый металл. 19 часов: * Раствор светло-фиолетовый, поверхность металла начала темнеть. День 2: * Окраска раствора усилилась. Большая часть поверхности никеля стала черной. День 3: * Окраска раствора усилилась. Большая часть поверхности никеля черная. День 4: * Темно-фиолетовый раствор. Большая часть поверхности никеля черная. Дни 5 и 6: * То же самое. День 9: * Окраска раствора усилилась. День 10: * Еще более темная окраска раствора. Преимущественно черная поверхность никеля. Дни 12 и 16: * То же. День 21: * Темно-фиолетовый, почти непрозрачный раствор. Большая часть поверхности никеля черная. Месяц 4: * Темно-фиолетовый раствор. Почти вся поверхность никеля черная. Дно и нижние участки стенок колбы покрылись зеленым налетом. |
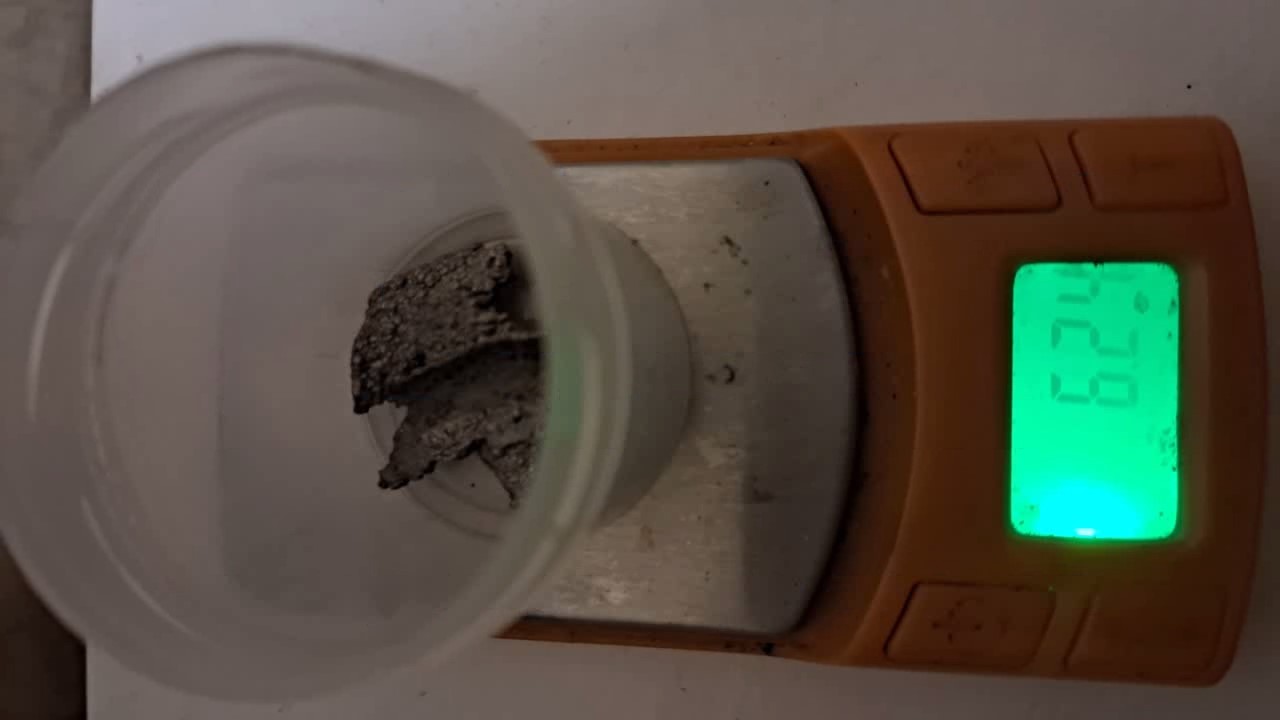

Dissolution of nickel metal in an aqueous ammonia solution |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|